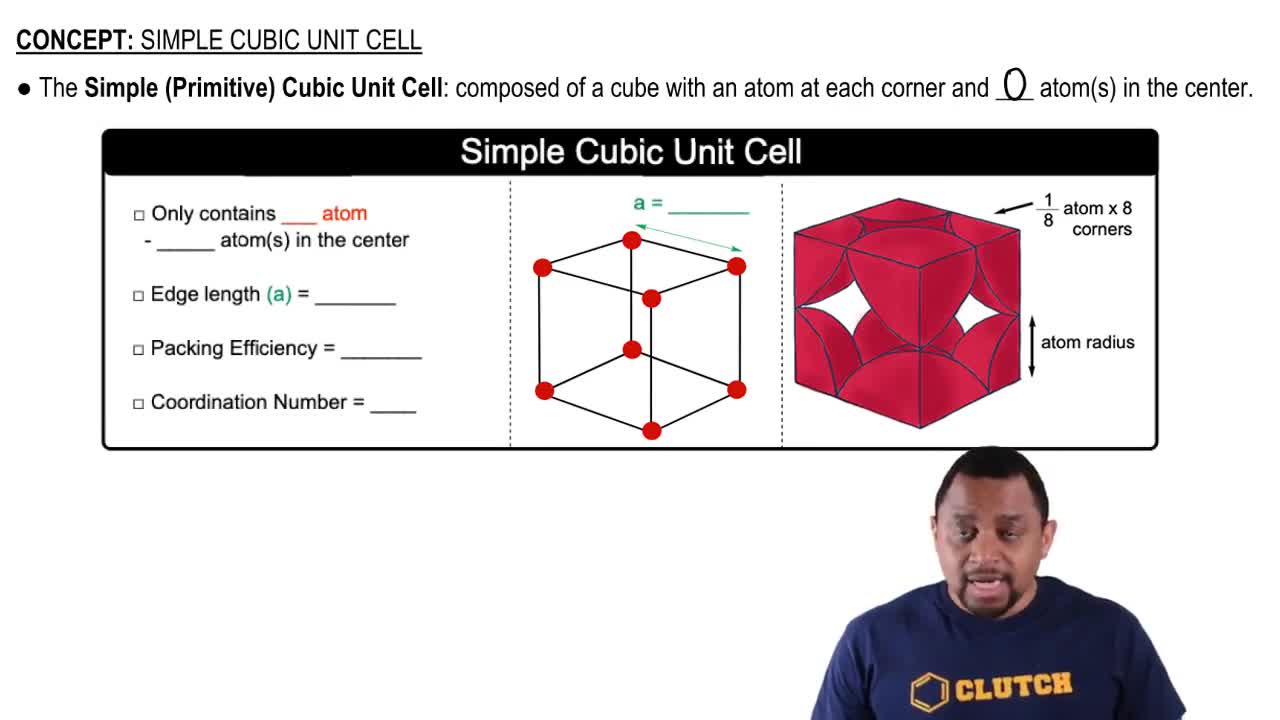
Textbook Question
If a protein can be induced to crystallize, its molecular structure can be determined by X-ray crystallography. Protein crystals, though solid, contain a large amount of water molecules along with the protein. The protein chicken egg-white lysozyme, for instance, crystallizes with a unit cell having angles of 90° and with edge lengths of 7.9 * 103 pm, 7.9 * 103 pm, and 3.8 * 103 pm. There are eight molecules in the unit cell. If the lysozyme molecule has a molecular weight of 1.44 * 104 and a density of 1.35 g>cm3, what percent of the unit cell is occupied by the protein?