Textbook Question
Two compounds (labeled I and II) have a liquid crystal state. Predict which compound has a higher temperature associ- ated with the solid to liquid crystal phase change. Explain your reasoning.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
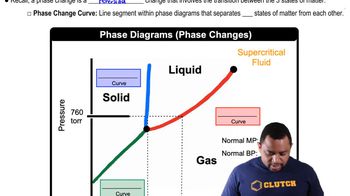
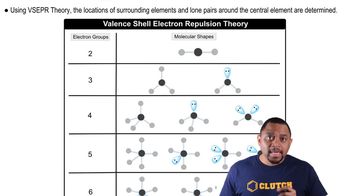
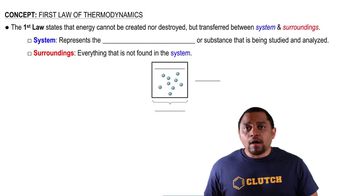
Two compounds (labeled I and II) have a liquid crystal state. Predict which compound has a higher temperature associ- ated with the solid to liquid crystal phase change. Explain your reasoning.