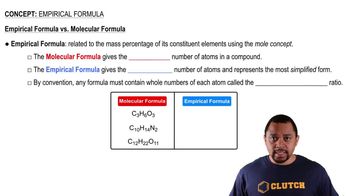
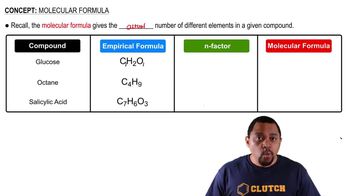
An empty 4.00-L steel vessel is filled with 1.00 atm of CH4(g) and 4.00 atm of O2(g) at 300 °C. A spark causes the CH4 to burn completely, according to the equation
CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) ΔH° = -802 kJ
(a) What mass of CO2(g) is produced in the reaction?