Textbook Question
One mole of an ideal gas has a volume of 22.414 L at STP. Assuming ideal behavior, what are the densities of the following gases in g/L at STP? (a) CH4 (b) CO2 (c) O2

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

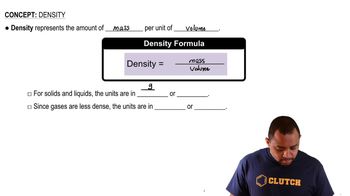

What are the molecular weights of the gases with the following densities: (b) 1.053 g/L at 25 °C and 752 mm Hg
Hydrogen gas can be prepared by reaction of zinc metal with aqueous HCl: Zn(s) + 2 HCl(aq) ¡ ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) (a) How many liters of H2 would be formed at 742 mm Hg and 15 °C if 25.5 g of zinc was allowed to react?