Assume that you have a cylinder with a movable piston. What would happen to the gas pressure inside the cylinder if you were to do the following? (b) Reduce the amount of gas by one-third while holding the temperature and volume constant

Assume that you have a cylinder with a movable piston. What would happen to the gas volume of the cylinder if you were to do the following? (c) Decrease the pressure by 75% at constant T?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Ideal Gas Law

Boyle's Law
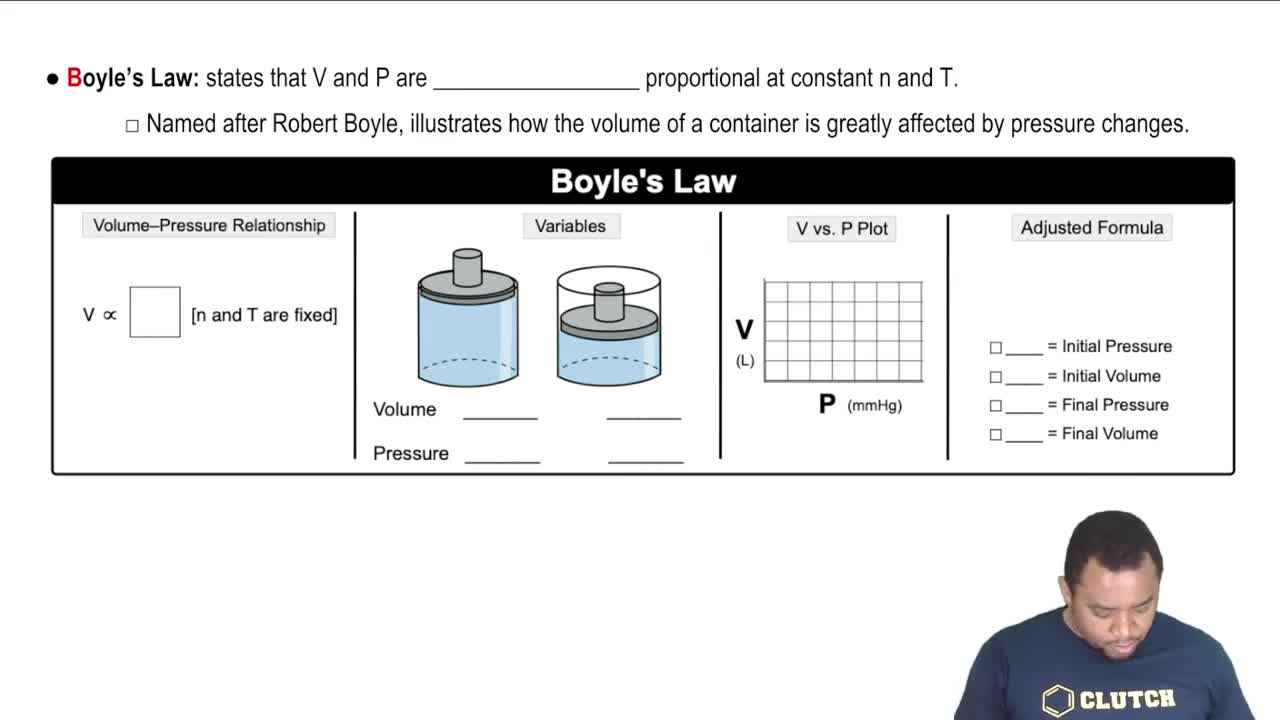
Gas Behavior at Constant Temperature

Assume that you have a cylinder with a movable piston. What would happen to the gas pressure inside the cylinder if you were to do the following? (c) Decrease the volume by 45% at constant T
Assume that you have a cylinder with a movable piston. What would happen to the gas pressure inside the cylinder if you were to do the following? (d) Halve the Kelvin temperature and triple the volume
Assume that you have a cylinder with a movable piston. What would happen to the gas volume of the cylinder if you were to do the following? (a) Halve the Kelvin temperature while holding the pressure constant
Assume that you have a cylinder with a movable piston. What would happen to the gas volume of the cylinder if you were to do the following? (b) Increase the amount of gas by one-fourth while holding the temperature and pressure constant
Assume that you have a cylinder with a movable piston. What would happen to the gas volume of the cylinder if you were to do the following? (d) Double the Kelvin temperature and double the pressure
