Textbook Question
What SI units are used for measuring the following quanti-ties? For derived units, express your answers in terms of the six fundamental units. (d) Volume
9
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

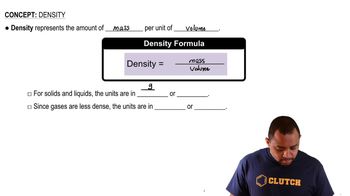

What SI units are used for measuring the following quanti-ties? For derived units, express your answers in terms of the six fundamental units. (d) Volume
What SI units are used for measuring the following quanti-ties? For derived units, express your answers in terms of the six fundamental units. (e) Energy
What SI units are used for measuring the following quanti-ties? For derived units, express your answers in terms of the six fundamental units. (e) Energy