In 1986 an electrical power plant in Taylorsville, Georgia, burned 8,376,726 tons of coal, a national record at that time. (a) Assuming that the coal was 83% carbon and 2.5% sulfur and that combustion was complete, calculate the number of tons of carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide produced by the plant during the year.

The standard enthalpies of formation of ClO and ClO2 are 101 and 102 kJ/mol, respectively. Using these data and the thermodynamic data in Appendix C, calculate the overall enthalpy change for each step in the following catalytic cycle: ClO(g) + O(g) → ClO(g) + O(g). What is the enthalpy change for the overall reaction that results from these two steps?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Enthalpy of Formation

Thermodynamic Cycle
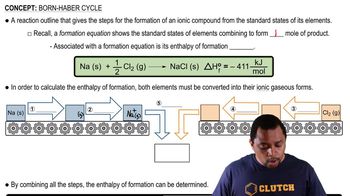
Hess's Law

The water supply for a midwestern city contains the following impurities: coarse sand, finely divided particulates, nitrate ions, trihalomethanes, dissolved phosphorus in the form of phosphates, potentially harmful bacterial strains, dissolved organic substances. Which of the following processes or agents, if any, is effective in removing each of these impurities: coarse sand filtration, activated carbon filtration, aeration, ozonization, precipitation with aluminum hydroxide?
he concentration of H2O in the stratosphere is about 5 ppm. It undergoes photodissociation according to:
H2O(𝑔)⟶H(𝑔)+OH(𝑔)
b.Given that the average bond enthalpy for an O−H bond is 463 kJ/mol, calculate the maximum wavelength for a photon that could cause this dissociation.
The following data were collected for the desturction of O3 by H (O3 + H → O2 + OH) at very low concentrations (b) Calculate the rate constant
The Henry's law constant for CO2 in water at 25 °C is 3.1x10^-2 M atm-1. (a) What is the soubility of CO2 in water at this temperature if the soltuion is in contact with air at normal atmospheric pressure?
