(a) What are trihalomethanes (THMs)? (b) Draw the Lewis structures of two example THMs.

Discuss how catalysts can make processes more energy efficient.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Catalysis
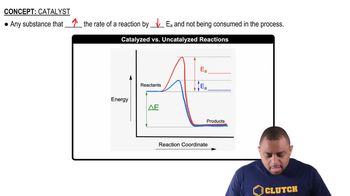
Activation Energy
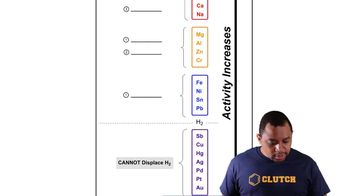
Energy Efficiency in Chemical Processes
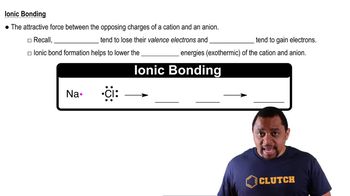
A reaction for converting ketones to lactones, called the Baeyer–Villiger reaction,
is used in the manufacture of plastics and pharmaceu- ticals. 3-Chloroperbenzoic acid is shock-sensitive, how- ever, and prone to explode. Also, 3-chlorobenzoic acid is a waste product. An alternative process being developed uses hydrogen peroxide and a catalyst consisting of tin deposited within a solid support. The catalyst is readily recovered from the reaction mixture. (a) What would you expect to be the other product of oxidation of the ketone to lactone by hydrogen peroxide?
In the following three instances, which choice is greener in a chemical process? Explain. (a) A reaction that can be run at 350 K for 12 h without a catalyst or one that can be run at 300 K for 1 h with a reusable catalyst.
Show how Equations 18.7 and 18.9, and the combination reaction that leads to the formation of molecular oxygen, 2O(𝑔)⟶O2(𝑔), can be added to give Equation 18.10.
