What is the hybridization of the central atom in c. SO3?
Ch.9 - Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 9, Problem 55c
Which of the following statements are true? c. A 𝜋 bond is made from the sideways overlap of two p orbitals.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the type of bond being discussed: a \( \pi \) bond.
Recall the definition of a \( \pi \) bond: it is formed by the sideways overlap of two parallel \( p \) orbitals.
Understand that \( \pi \) bonds are different from \( \sigma \) bonds, which are formed by the head-on overlap of orbitals.
Consider the orientation of \( p \) orbitals: they have lobes that can overlap sideways to form a \( \pi \) bond.
Conclude that the statement is true based on the definition and characteristics of \( \pi \) bonds.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
46sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Bonding Orbitals
Bonding orbitals are regions in a molecule where the probability of finding electrons is high, resulting from the overlap of atomic orbitals. In covalent bonding, these orbitals can be classified as sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds, which differ in their formation and electron distribution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
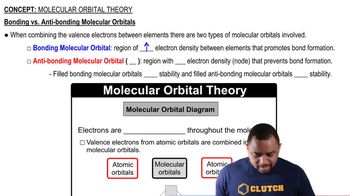
Molecular Orbital Theory
Pi Bonds
A pi (π) bond is a type of covalent bond that occurs when two atomic orbitals overlap sideways, typically involving p orbitals. This overlap allows for the sharing of electrons above and below the bond axis, contributing to the overall stability and geometry of the molecule.
Recommended video:
Guided course
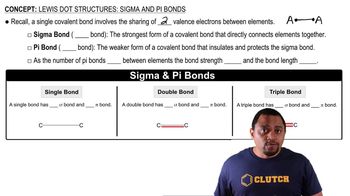
Lewis Dot Structures: Sigma & Pi Bonds
Orbital Hybridization
Orbital hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals that can explain the geometry of molecular bonding. For example, in the case of double bonds, one σ bond is formed from head-on overlap, while the π bond arises from the lateral overlap of unhybridized p orbitals.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Hybridization
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
What is the hybridization of the central atom in d. TeCl2?
Textbook Question
Shown here are three pairs of hybrid orbitals, with each set at a characteristic angle. For each pair, determine the type of hybridization, if any, that could lead to hybrid orbitals at the specified angle. (a)
(b)
(c)
Textbook Question
Which of the following statements are true? d. A 𝜋 bond has two regions of overlap on opposite sides of the internuclear axis.
Textbook Question
(b) Imagine that you could hold two atoms that are bonded together, twist them, and not change the bond length. Would it be easier to twist (rotate) around a single s bond or around a double 1s plus p2 bond, or would they be the same?
Textbook Question
(b) What is the hybridization of the carbon atoms in each molecule?
1
views
