Textbook Question
Consider the following Lewis structure:
a. Does the Lewis structure depict a neutral molecule or an ion? If it is an ion, what is the charge on the ion?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Consider the following Lewis structure:
a. Does the Lewis structure depict a neutral molecule or an ion? If it is an ion, what is the charge on the ion?
Predict the molecular geometry of each of the following molecules: (b) H O C O C O O H
What hybridization do you expect for the atom indicated in red in each of the following species? (a) CH3CO2-
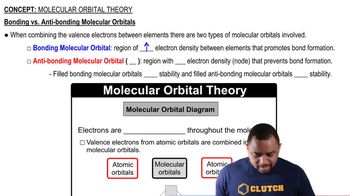
Consider the H2+ ion. (a) Sketch the molecular orbitals of the ion and draw its energy-level diagram.
Consider the H2+ ion. (b) How many electrons are there in the H2+ ion?
Consider the H2+ ion. (c) Write the electron configuration of the ion in terms of its MOs. (d) What is the bond order in H2+?