(c) With what neutral homonuclear diatomic molecules are the NO+ and NO- ions isoelectronic (same number of electrons)? With what neutral homonuclear diatomic molecule is the NO- ion isoelectronic (same number of electrons)?

Assume that the MOs of diatomics from the third row of the periodic table, such as P2, are analogous to those from the second row.
a. Which valence atomic orbitals of P are used to construct the MOs of P2?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Molecular Orbitals (MOs)
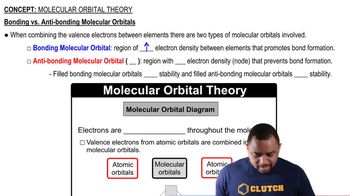
Valence Atomic Orbitals
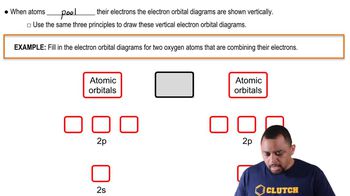
Periodic Trends in Orbital Energy

Determine the electron configurations for CN+, CN, and CN-. (a) Which species has the strongest C¬N bond?
Determine the electron configurations for CN+, CN, and CN-. b. Which species, if any, is paramagnetic?
Assume that the MOs of diatomics from the third row of the periodic table, such as P2, are analogous to those from the second row.
c. For the P2 molecule, how many electrons occupy the MO in the figure?
The iodine bromide molecule, IBr, is an interhalogen compound. Assume that the molecular orbitals of IBr are analogous to the homonuclear diatomic molecule F2. (a) Which valence atomic orbitals of I and of Br are used to construct the MOs of IBr?
The iodine bromide molecule, IBr, is an interhalogen compound. Assume that the molecular orbitals of IBr are analogous to the homonuclear diatomic molecule F2. (c) One of the valence MOs of IBr is sketched here. Determine whether each of the following statements about this orbital is true: i. This is an antibonding orbital. ii. The larger contribution is from the I atom. iii. The energy of the molecular orbital is closer in energy to the valence atomic orbitals of Br than to those of I.
