NaCl and KF have the same crystal structure. The only difference between the two is the distance that separates cations and anions. (a) The lattice energies of NaCl and KF are given in Table 8.1. Based on the lattice energies, would you expect the Na─Cl or the K─F distance to be longer?

The substances NaF and CaO are isoelectronic (have the same number of valence electrons). (b) What are the charges of each of the anions in each compound?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Isoelectronic Species
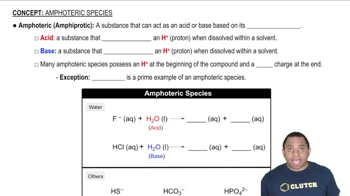
Valence Electrons
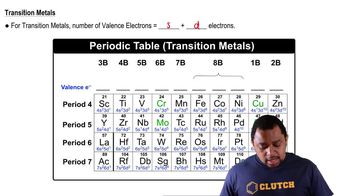
Ionic Charges

NaCl and KF have the same crystal structure. The only difference between the two is the distance that separates cations and anions. (b) Use the ionic radii given in Figure 7.8 to estimate the Na─Cl and K─F distances.
The substances NaF and CaO are isoelectronic (have the same number of valence electrons). (a) What are the charges on each of the cations in each compound?
The substances NaF and CaO are isoelectronic (have the same number of valence electrons). (d) Using the lattice energies in Table 8.1, predict the lattice energy of ScN.
(a) Does the lattice energy of an ionic solid increase or decrease (i) as the charges of the ions increase, (ii) as the sizes of the ions increase?
Consider the ionic compounds KF, NaCl, NaBr, and LiCl. (a) Use ionic radii (Figure 7.8) to estimate the cation–anion distance for each compound.
