Draw the Lewis structures for each of the following molecules or ions. Identify instances where the octet rule is not obeyed; state which atom in each compound does not follow the octet rule; and state how many electrons surround these atoms: a. NO, b. BF3, c. ICl2−, d. OPBr3 (the P is the central atom), e. XeF4.

In the vapor phase, BeCl2 exists as a discrete molecule. (a) Draw the Lewis structure of this molecule, using only single bonds. Does this Lewis structure satisfy the octet rule?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Lewis Structure

Octet Rule

Molecular Geometry
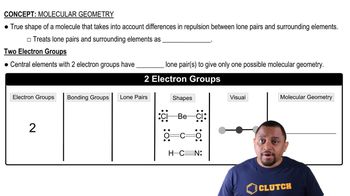
In the vapor phase, BeCl2 exists as a discrete molecule. (c) On the basis of the formal charges, which Lewis structure is expected to be dominant for BeCl2?
(a) Describe the molecule xenon trioxide, XeO3, using four possible Lewis structures, one each with zero, one, two, or three Xe¬O double bonds. (b) Do any of these resonance structures satisfy the octet rule for every atom in the molecule? (c) Do any of the four Lewis structures have multiple resonance structures? If so, how many resonance structures do you find? (d) Which of the Lewis structures in part (a) yields the most favorable formal charges for the molecule?
There are many Lewis structures you could draw for sulfuric acid, H2SO4 (each H is bonded to an O). (a) What Lewis structure(s) would you draw to satisfy the octet rule?
