Textbook Question
Consider the element silicon, Si. (c) Which subshells hold the valence electrons?
2
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
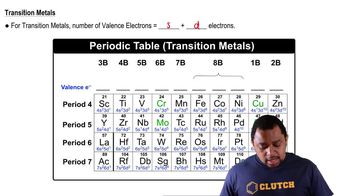
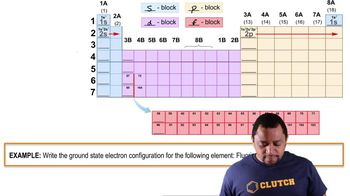

Consider the element silicon, Si. (c) Which subshells hold the valence electrons?
(a) Write the electron configuration for the element titanium, Ti. How many valence electrons does this atom possess?
(b) Hafnium, Hf, is also found in group 4. Write the electron configuration for Hf.
Write the Lewis symbol for atoms of each of the following elements: (a) Te (b) Si (c) Ar (d) P
What is the Lewis symbol for each of the following atoms or ions: c. Sn2+
(a) Using Lewis symbols, make a sketch of the reaction between magnesium and oxygen atoms to give the ionic substance MgO