Textbook Question
Pick the correct word to complete the sentence: The larger the atom, the (smaller/larger) its first ionization energy.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


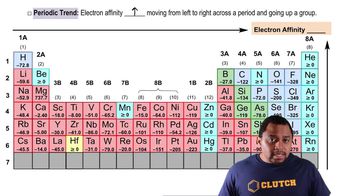
Pick the correct word to complete the sentence: The larger the atom, the (smaller/larger) its first ionization energy.
Which element in the periodic table has the largest first ionization energy?
Consider the following equation:
Ca+(𝑔)+e−⟶Ca(𝑔)
Which of the following statements are true?
i. The energy change for this process is the electron affinity of the Ca+ ion.
ii. The energy change for this process is the negative of the first ionization energy of the Ca atom.
iii. The energy change for this process is the negative of the electron affinity of the Ca atom.
a. Only statement i is true.
b. Only statement ii is true.
c. Only statement iii is true.
d. Only statements i and ii are true.
e. All three statements are true.