We will see in Chapter 12 that semiconductors are materials that conduct electricity better than nonmetals but not as well as metals. The only two elements in the periodic table that are technologically useful semiconductors are silicon and germanium. Integrated circuits in computer chips today are based on silicon. Compound semiconductors are also used in the electronics industry. Examples are gallium arsenide, GaAs; gallium phosphide, GaP; cadmium sulfide, CdS; and cadmium selenide, CdSe. (b) Workers in the semiconductor industry refer to 'II–VI' and 'III–V' materials, using Roman numerals. Can you identify which compound semiconductors are II–VI and which are III–V? (c) Suggest other compositions of compound semiconductors based on the positions of their elements in the periodic table.

Moseley established the concept of atomic number by studying X rays emitted by the elements. The X rays emitted by some of the elements have the following wavelengths: Element Wavelength (pm) Ne 1461 Ca 335.8 Zn 143.5 Zr 78.6 Sn 49.1 (d) Use the result from part (b) to predict the X-ray wavelength emitted by iron.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
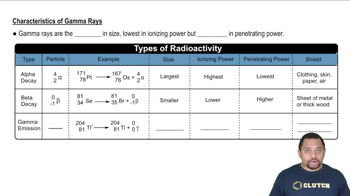
Atomic Number

X-ray Emission
Wavelength and Energy Relationship
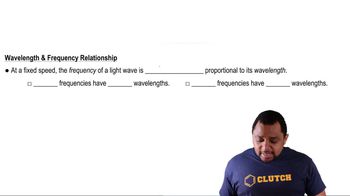
Moseley established the concept of atomic number by studying X rays emitted by the elements. The X rays emitted by some of the elements have the following wavelengths: Element Wavelength (pm) Ne 1461 Ca 335.8 Zn 143.5 Zr 78.6 Sn 49.1 (a) Calculate the frequency, n, of the X rays emitted by each of the elements, in Hz.
Moseley established the concept of atomic number by studying X rays emitted by the elements. The X rays emitted by some of the elements have the following wavelengths: Element Wavelength (pm) Ne 1461 Ca 335.8 Zn 143.5 Zr 78.6 Sn 49.1 (b) Plot the square root of n versus the atomic number of the element. What do you observe about the plot? (e) A particular element emits X rays with a wavelength of 98.0 pm. What element do you think it is?
One way to measure ionization energies is ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (PES), a technique based on the photoelectric effect. (Section 6.2) In PES, monochromatic light is directed onto a sample, causing electrons to be emitted. The kinetic energy of the emitted electrons is measured. The difference between the energy of the photons and the kinetic energy of the electrons corresponds to the energy needed to remove the electrons (that is, the ionization energy). Suppose that a PES experiment is performed in which mercury vapor is irradiated with ultraviolet light of wavelength 58.4 nm. (c) The kinetic energy of the emitted electrons is measured to be 1.72 × 10-18 J. What is the first ionization energy of Hg, in kJ/mol?
One way to measure ionization energies is ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (PES), a technique based on the photoelectric effect. (Section 6.2) In PES, monochromatic light is directed onto a sample, causing electrons to be emitted. The kinetic energy of the emitted electrons is measured. The difference between the energy of the photons and the kinetic energy of the electrons corresponds to the energy needed to remove the electrons (that is, the ionization energy). Suppose that a PES experiment is performed in which mercury vapor is irradiated with ultraviolet light of wavelength 58.4 nm. (d) Using Figure 7.10, determine which of the halogen elements has a first ionization energy closest to that of mercury.
When magnesium metal is burned in air (Figure 3.5), two products are produced. One is magnesium oxide, MgO. The other is the product of the reaction of Mg with molecular nitrogen, magnesium nitride. When water is added to magnesium nitride, it reacts to form magnesium oxide and ammonia gas. c. In an experiment, a piece of magnesium ribbon is burned in air in a crucible. The mass of the mixture of MgO and magnesium nitride after burning is 0.470 g. Water is added to the crucible, further reaction occurs, and the crucible is heated to dryness until the final product is 0.486 g of MgO. What was the mass percentage of magnesium nitride in the mixture obtained after the initial burning?
