It is possible to define metallic character as we do in this book and base it on the reactivity of the element and the ease with which it loses electrons. Alternatively, one could measure how well electricity is conducted by each of the elements to determine how 'metallic' the elements are. On the basis of conductivity, there is not much of a trend in the periodic table: Silver is the most conductive metal, and manganese the least. Look up the first ionization energies of silver and manganese; which of these two elements would you call more metallic based on the way we define it in this book?

(a) One of the alkali metals reacts with oxygen to form a solid white substance. When this substance is dissolved in water, the solution gives a positive test for hydrogen peroxide, H2O2. When the solution is tested in a burner flame, a lilac-purple flame is produced. What is the likely identity of the metal? (b) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of the white substance with water.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Alkali Metals
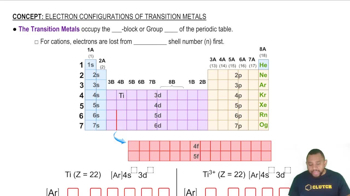
Hydrogen Peroxide Formation

Flame Test
Which of the following is the expected product of the reaction of K(s) and H2(g)? (i) KH(s), (ii) K2H(s), (iii) KH2(s), (iv) K2H2(s), or (v) K(s) and H2(g) will not react with one another.
A historian discovers a nineteenth-century notebook in which some observations, dated 1822, were recorded on a substance thought to be a new element. Here are some of the data recorded in the notebook: 'Ductile, silver-white, metallic looking. Softer than lead. Unaffected by water. Stable in air. Melting point: 153 °C. Density: 7.3 g>cm3. Electrical conductivity: 20% that of copper. Hardness: About 1% as hard as iron. When 4.20 g of the unknown is heated in an excess of oxygen, 5.08 g of a white solid is formed. The solid could be sublimed by heating to over 800 °C.' (a) Using information in the text and the CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, and making allowances for possible variations in numbers from current values, identify the element reported.
We will see in Chapter 12 that semiconductors are materials that conduct electricity better than nonmetals but not as well as metals. The only two elements in the periodic table that are technologically useful semiconductors are silicon and germanium. Integrated circuits in computer chips today are based on silicon. Compound semiconductors are also used in the electronics industry. Examples are gallium arsenide, GaAs; gallium phosphide, GaP; cadmium sulfide, CdS; and cadmium selenide, CdSe. (a) What is the relationship between the compound semiconductors' compositions and the positions of their elements on the periodic table relative to Si and Ge?
