(d) How many kJ of heat are needed to raise the temperature of 10.00 kg of liquid water from 24.6 to 46.2 °C?

The specific heat of ethanol, C2H5OH(l), is 2.44 J•g/K. b. Which will require more heat, increasing the temperature of 1 mol of C2H5OH(𝑙) by a certain amount or increasing the temperature of 1 mol of H2O(𝑙) by the same amount?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Specific Heat Capacity
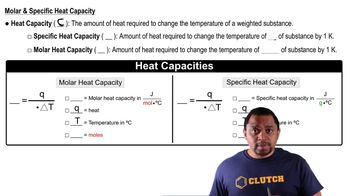
Molar Mass and Moles

Heat Transfer Equation

(b) Calculate the energy needed for this temperature change.
The specific heat of ethanol, C2H5OH(l), is 2.44 J•g/K. (a) How many J of heat are needed to raise the temperature of 80.0 g of octane from 10.0 to 25.0 °C?
Consider the data about gold metal in Exercise 5.24(b). b. Suppose that the same amount of heat is added to two 10.0-g blocks of metal, both initially at the same temperature. One block is gold metal, and the other is iron metal. Which block will have the greater rise in temperature after addition of the heat?
Consider the data about gold metal in Exercise 5.24(b). c. What is the molar heat capacity of Au(s)?
When a 5.10-g sample of solid sodium hydroxide dissolves in 100.0 g of water in a coffee-cup calorimeter (Figure 5.18), the temperature rises from 20.5 to 33.2 °C. a. Calculate the quantity of heat (in kJ) released in the reaction.
