Suppose you have 5.00 g of powdered magnesium metal, 1.00 L of 2.00 M potassium nitrate solution, and 1.00 L of 2.00 M silver nitrate solution. d. What is the molarity of the Mg2+ ions in the resulting solution?
Ch.4 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 4, Problem 105
A fertilizer railroad car carrying 129,840 L of commercial aqueous ammonia (30% ammonia by mass) tips over and spills. The density of the aqueous ammonia solution is 0.88 g/cm³. What mass of citric acid, C₆H₈O₇ (which contains three acidic protons), is required to neutralize the spill?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Convert the volume of the aqueous ammonia solution from liters to cubic centimeters (cm³) using the conversion factor 1 L = 1000 cm³.
Calculate the mass of the aqueous ammonia solution using the formula: mass = volume × density. Use the density provided (0.88 g/cm³) and the volume in cm³.
Determine the mass of ammonia (NH₃) in the solution by using the percentage by mass (30%). Multiply the total mass of the solution by 0.30.
Write the balanced chemical equation for the neutralization reaction between ammonia (NH₃) and citric acid (C₆H₈O₇). Each mole of citric acid can neutralize three moles of ammonia.
Calculate the moles of ammonia using its molar mass (17.03 g/mol), then use the stoichiometry from the balanced equation to find the moles of citric acid needed. Finally, convert the moles of citric acid to mass using its molar mass (192.12 g/mol).
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions. It involves using balanced chemical equations to determine the proportions of substances involved. In this case, stoichiometry will help calculate how much citric acid is needed to neutralize the ammonia based on their reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Stoichiometry Concept
Acid-Base Neutralization
Acid-base neutralization is a chemical reaction where an acid reacts with a base to produce water and a salt. In this scenario, citric acid (an acid) will react with ammonia (a base) to form ammonium citrate and water. Understanding the nature of this reaction is crucial for determining the amount of citric acid required.
Recommended video:
Guided course
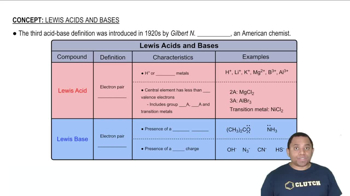
Lewis Acids and Bases
Concentration and Density Calculations
Concentration refers to the amount of solute in a given volume of solution, while density is the mass per unit volume of a substance. To find the mass of ammonia in the spill, one must use the density of the solution and its volume. This mass will then be used in stoichiometric calculations to find the required mass of citric acid.
Recommended video:
Guided course
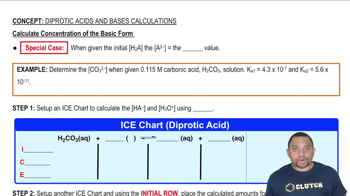
Calculate Concentration of the Basic Form
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
(a) By titration, 15.0 mL of 0.1008 M sodium hydroxide is needed to neutralize a 0.2053-g sample of a weak acid. What is the molar mass of the acid if it is monoprotic?
Textbook Question
(b) An elemental analysis of the acid indicates that it is composed of 5.89% H, 70.6% C, and 23.5% O by mass. What is its molecular formula?
Textbook Question
Suppose you have 5.00 g of powdered magnesium metal, 1.00 L of 2.00 M potassium nitrate solution, and 1.00 L of 2.00 M silver nitrate solution. a. Which one of the solutions will react with the magnesium powder?
Textbook Question
A sample of 7.75 g of Mg(OH)2 is added to 25.0 mL of 0.200 𝑀 HNO3. c. How many moles of Mg(OH)2,HNO3, and Mg(NO3)2 are present after the reaction is complete?
