When ethane 1C2H62 reacts with chlorine 1Cl22, the main product is C2H5Cl, but other products containing Cl, such as C2H4Cl2, are also obtained in small quantities. The formation of these other products reduces the yield of C2H5Cl. (a) Calculate the theoretical yield of C2H5Cl when 125 g of C2H6 reacts with 255 g of Cl2, assuming that C2H6 and Cl2 react only to form C2H2Cl and HCl. (b) Calculate the percent yield of C2H5Cl if the reaction produces 206 g of C2H5Cl.

Write the balanced chemical equations for a. the complete combustion of acetic acid (CH3COOH), the main ingredient in vinegar;
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Combustion Reactions
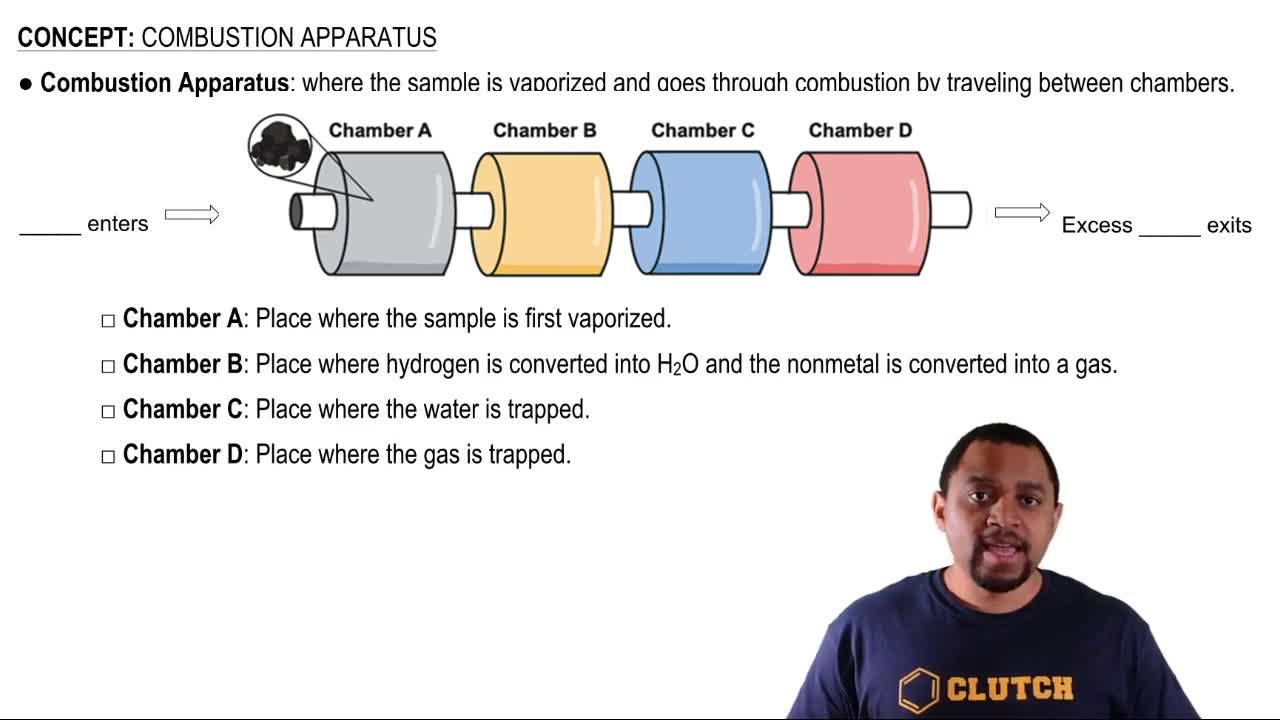
Balancing Chemical Equations

Stoichiometry

Hydrogen sulfide is an impurity in natural gas that must be removed. One common removal method is called the Claus process, which relies on the reaction: 8 H2S1g2 + 4 O21g2¡S81l2 + 8 H2O1g2 Under optimal conditions the Claus process gives 98% yield of S8 from H2S. If you started with 30.0 g of H2S and 50.0 g of O2, how many grams of S8 would be produced, assuming 98% yield?
When hydrogen sulfide gas is bubbled into a solution of sodium hydroxide, the reaction forms sodium sulfide and water. How many grams of sodium sulfide are formed if 1.25 g of hydrogen sulfide is bubbled into a solution containing 2.00 g of sodium hydroxide, assuming that the sodium sulfide is made in 92.0% yield?
Write the balanced chemical equations for c. the combination reaction between nickel metal and chlorine gas.
The effectiveness of nitrogen fertilizers depends on both their ability to deliver nitrogen to plants and the amount of nitrogen they can deliver. Four common nitrogen-containing fertilizers are ammonia, ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, and urea [(NH2)2CO] Rank these fertilizers in terms of the mass percentage nitrogen they contain.
b. How many molecules of C9H8O4 are in this tablet?
