Serotonin is a compound that conducts nerve impulses in the brain. It contains 68.2% C, 6.86% H, 15.9% N, and 9.08% O. Its molar mass is 176 g/mol Determine its molecular formula.

A compound, KBrO𝑥, where x is unknown, is analyzed and found to contain 52.92% Br. What is the value of x?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Molar Mass and Percent Composition

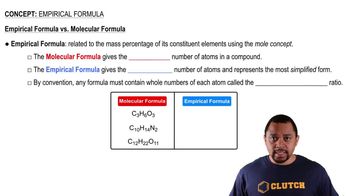
Empirical Formula
Stoichiometry

Vanillin, the dominant flavoring in vanilla, contains C, H, and O. When 1.05 g of this substance is completely combusted, 2.43 g of CO2 and 0.50 g of H2O are produced. What is the empirical formula of vanillin?
An organic compound was found to contain only C, H, and Cl. When a 1.50-g sample of the compound was completely combusted in air, 3.52 g of CO2 was formed. In a separate experiment, the chlorine in a 1.00-g sample of the compound was converted to 1.27 g of AgCl. Determine the empirical formula of the compound.
An element X forms an iodide (XI3) and a chloride (XCl3). The iodide is quantitatively converted to the chloride when it is heated in a stream of chlorine: 2 XI3 + 3 Cl2 → 2 XCl3 + 3 I2 If 0.5000 g of XI3 is treated with chlorine, 0.2360 g of XCl3 is obtained. (a) Calculate the atomic weight of the element X. (b) Identify the element X.
A method used by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for determining the concentration of ozone in air is to pass the air sample through a 'bubbler' containing sodium iodide, which removes the ozone according to the following equation: O31g2 + 2 NaI1aq2 + H2O1l2¡ O21g2 + I21s2 + 2 NaOH1aq2 (a) How many moles of sodium iodide are needed to remove 5.95 * 10-6 mol of O3?
A method used by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for determining the concentration of ozone in air is to pass the air sample through a 'bubbler' containing sodium iodide, which removes the ozone according to the following equation: O31g2 + 2 NaI1aq2 + H2O1l2¡ O21g2 + I21s2 + 2 NaOH1aq2 (b) How many grams of sodium iodide are needed to remove 1.3 mg of O3?
