Textbook Question
The lobes of which d orbitals point directly between the ligands in a. octahedral geometry,

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

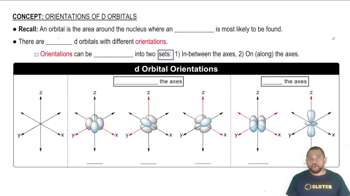
The lobes of which d orbitals point directly between the ligands in a. octahedral geometry,
The lobes of which d orbitals point directly between the ligands in b. tetrahedral geometry?
As shown in Figure 23.26, the d-d transition of [Ti(H2O)6]³⁺ produces an absorption maximum at a wavelength of about 500 nm .
a. What is the magnitude of ∆ for [Ti(H2O)6]³⁺ in kJ/mol?
b. How would the magnitude of ∆ change if the H2O ligands in [Ti(H2O)6]]³⁺ were placed with NH3 ligands?