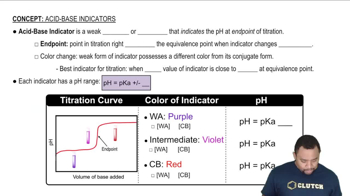
Photon Energy and Wavelength Relationship
The energy of a photon is inversely related to its wavelength, described by the equation E = hc/λ, where E is energy, h is Planck's constant, c is the speed of light, and λ is the wavelength. This relationship indicates that shorter wavelengths correspond to higher energy photons. For a wavelength of 610 nm, this equation can be used to calculate the energy in joules.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance