Ch.22 - Chemistry of the Nonmetals

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 22, Problem 68
Complete the exercises below. Write a balanced equation for each of the following reactions: a. Burning magnesium metal in a carbon dioxide atmosphere reduces the CO₂ to carbon. b. In photosynthesis, solar energy is used to produce glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and O₂ from carbon dioxide and water.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the reactants and products for each reaction. For reaction (a), the reactants are magnesium (Mg) and carbon dioxide (CO₂), and the products are magnesium oxide (MgO) and carbon (C). For reaction (b), the reactants are carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O), and the products are glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) and oxygen (O₂).
Step 2: Write the unbalanced chemical equations for each reaction. For reaction (a), the unbalanced equation is: Mg + CO₂ → MgO + C. For reaction (b), the unbalanced equation is: CO₂ + H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + O₂.
Step 3: Balance the equation for reaction (a). Start by balancing the number of magnesium atoms, then balance the carbon atoms, and finally balance the oxygen atoms. Adjust coefficients as necessary to ensure the same number of each type of atom on both sides of the equation.
Step 4: Balance the equation for reaction (b). Begin by balancing the carbon atoms, then balance the hydrogen atoms, and finally balance the oxygen atoms. Adjust coefficients to ensure the same number of each type of atom on both sides of the equation.
Step 5: Verify that both equations are balanced by counting the number of each type of atom on both sides of the equations. Ensure that the law of conservation of mass is satisfied, meaning the total mass of reactants equals the total mass of products.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations is essential to ensure that the law of conservation of mass is upheld, meaning the number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the equation. This involves adjusting coefficients in front of compounds to achieve equal numbers of each type of atom, reflecting the actual stoichiometry of the reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Balancing Chemical Equations
Combustion Reactions
Combustion reactions involve the reaction of a substance with oxygen, typically producing heat and light. In the case of magnesium burning in carbon dioxide, it serves as a reduction reaction where magnesium reduces CO₂ to carbon, showcasing the transfer of electrons and the formation of new products.
Recommended video:
Guided course
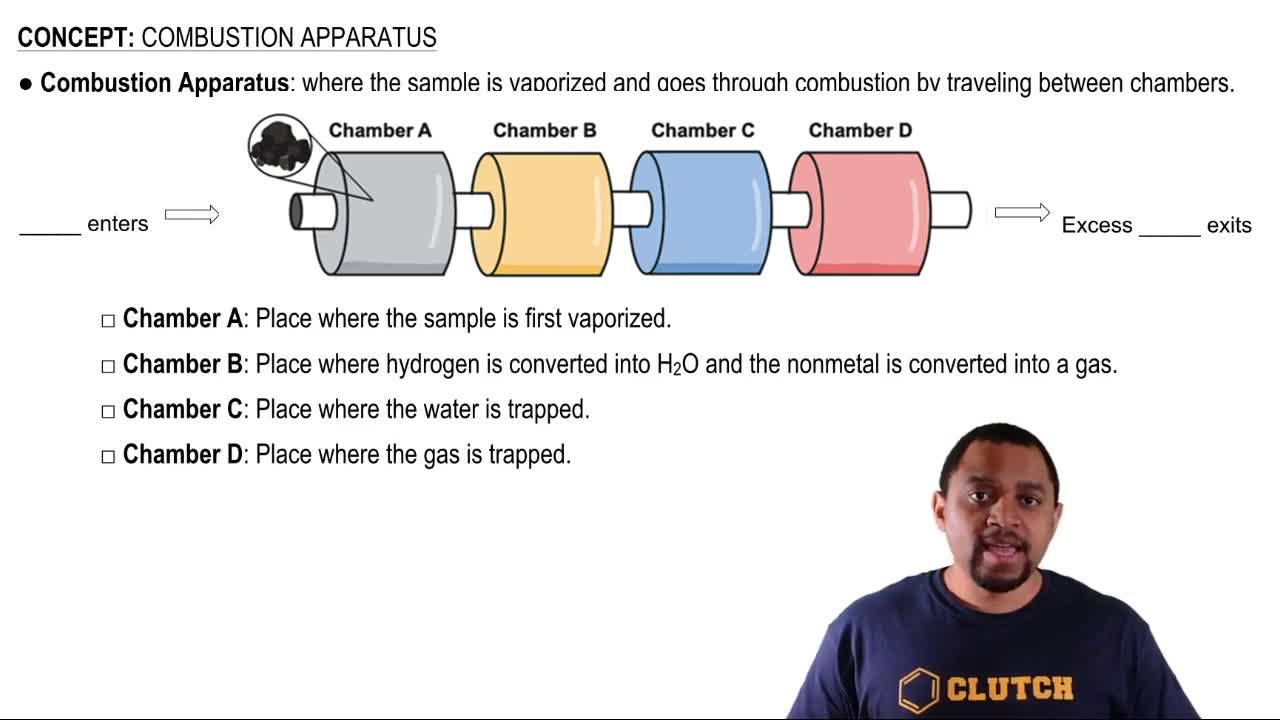
Combustion Apparatus
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a biochemical process where plants convert light energy into chemical energy, producing glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water. This process can be summarized by a balanced equation, highlighting the transformation of reactants into products and the importance of energy transfer in biological systems.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Spontaneity of Processes Example
Related Practice
