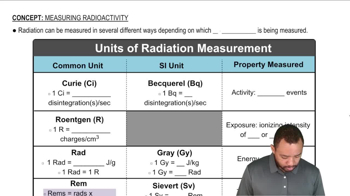
Energy Deposition and Radiation Units
When radioactive decay occurs, energy is released in the form of radiation, which can be quantified in joules. The energy deposited by radiation in biological tissues is measured in rads, where 1 rad equals the absorption of 0.01 joules of energy per kilogram of tissue. The rem is a unit that accounts for the biological effect of radiation, factoring in the type of radiation and its impact on human health.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance