Iodine-131 is a convenient radioisotope to monitor thyroid activity in humans. It is a beta emitter with a half-life of 8.02 days. The thyroid is the only gland in the body that uses iodine. A person undergoing a test of thyroid activity drinks a solution of NaI, in which only a small fraction of the iodide is radioactive. b. A normal thyroid will take up about 12% of the ingested iodide in a few hours. How long will it take for the radioactive iodide taken up and held by the thyroid to decay to 0.01% of the original amount?
Ch.21 - Nuclear Chemistry

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 21, Problem 57
(a) Which of the following are required characteristics of an isotope to be used as a fuel in a nuclear power reactor? (i) It must emit gamma radiation. (ii) On decay, it must release two or more neutrons. (iii) It must have a half-life of less than one hour. (iv) It must undergo fission upon the absorption of a neutron. (b) What is the most common fissionable isotope in a commercial nuclear power reactor?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the role of isotopes in nuclear reactors. Isotopes used as fuel in nuclear reactors must be capable of sustaining a chain reaction. This typically involves the isotope undergoing fission when it absorbs a neutron, releasing energy and additional neutrons.
Step 2: Evaluate each characteristic for part (a): (i) Emitting gamma radiation is not a requirement for an isotope to be used as fuel. (ii) Releasing two or more neutrons upon decay is important for sustaining a chain reaction, as these neutrons can induce fission in other nuclei. (iii) A half-life of less than one hour is impractical for reactor fuel, as it would decay too quickly. (iv) Undergoing fission upon neutron absorption is crucial for the isotope to be used as fuel.
Step 3: Identify the most common fissionable isotope for part (b). In commercial nuclear power reactors, the most common fissionable isotope is Uranium-235 (\(^{235}\text{U}\)). It is capable of sustaining a chain reaction and is used in most nuclear reactors.
Step 4: Consider the properties of Uranium-235. \(^{235}\text{U}\) undergoes fission when it absorbs a neutron, releasing energy and additional neutrons, which can then induce fission in other \(^{235}\text{U}\) nuclei, sustaining the chain reaction.
Step 5: Summarize the key characteristics of a suitable isotope for nuclear fuel: It should undergo fission upon neutron absorption and release multiple neutrons to sustain a chain reaction. The most common isotope used is \(^{235}\text{U}\).
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isotopes and Nuclear Fission
Isotopes are variants of a chemical element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. In nuclear fission, certain isotopes can split into smaller nuclei when they absorb a neutron, releasing a significant amount of energy. This process is essential for nuclear reactors, as it provides the energy needed for electricity generation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
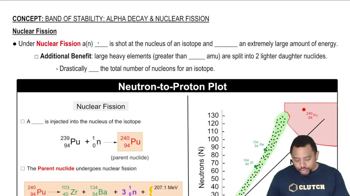
Band of Stability: Nuclear Fission
Characteristics of Fissionable Isotopes
For an isotope to be effective as a nuclear fuel, it must possess specific characteristics. It should undergo fission upon neutron absorption, ideally release additional neutrons to sustain a chain reaction, and have a suitable half-life that balances stability and reactivity. These properties ensure efficient energy production and safety in reactor operations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Isotopes
Common Fissionable Isotopes
The most common fissionable isotope used in commercial nuclear power reactors is Uranium-235 (U-235). This isotope is favored due to its ability to sustain a chain reaction and its relative abundance compared to other fissionable materials. U-235 is typically enriched from natural uranium, which contains a much lower percentage of this isotope.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Isotopes
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Why is it important that radioisotopes used as diagnostic tools in nuclear medicine produce gamma radiation when they decay? Why are alpha emitters not used as diagnostic tools?
Textbook Question
(c) What other substances are used as a moderator in nuclear reactor designs?
1
views
