Complete and balance the following equations, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents: (a) Cr2O72-(aq) + I-(aq) → Cr3+(aq) + IO3-(aq) (acidic solution) (b) MnO4-(aq) + CH3O(1aq) → Mn2+(aq) + HCOOH(aq) (acidic solution) (c) I2(s) + OCl-(aq) → IO3-(aq) + Cl-(aq) (acidic solution)

Complete and balance the following equations, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents: As2O3(s) + NO3-(aq) → H3AsO4(aq) + N2O3(aq) (acidic solution)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Redox Reactions
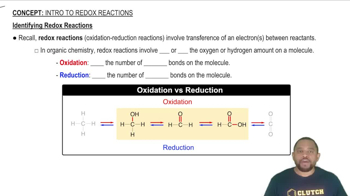
Balancing Chemical Equations

Identifying Oxidizing and Reducing Agents

Complete and balance the following equations, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents: MnO4-(aq) + Br-(aq) → MnO2(s) + BrO3-(aq) (basic solution)
Complete and balance the following equations, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents:
a. MnO4−(𝑎𝑞)+CH3OH(𝑎𝑞)⟶Mn2+(𝑎𝑞)+HCOOH(𝑎𝑞)(acidic solution)
b. As2O3(𝑠)+NO3−(𝑎𝑞)⟶H3AsO4(𝑎𝑞)+N2O3(𝑎𝑞)(acidic solution)
c. Pb(OH)42−(𝑎𝑞)+ClO−(𝑎𝑞)⟶PbO2(𝑠)+Cl−(𝑎𝑞)(basic solution)
Complete and balance the following equations, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents. (Recall that the O atoms in hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, have an atypical oxidation state.) (a) NO2-(aq) + Cr2O72-(aq) → Cr3+(aq) + NO3-(aq) (acidic solution) (b) S(s) + HNO3(aq) → H2SO3(aq) + N2O(g) (acidic solution) (c) Cr2O72- (aq) + CH3OH(aq) → HCOOH(aq) + Cr3+(aq) (acidic solution) (d) BrO3-(aq) + N2H4(g) → Br-(aq) + N2(g) (acidic solution)
Complete and balance the following equations, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents. (Recall that the O atoms in hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, have an atypical oxidation state.)
a. S(s) + HNO3(aq) → H2SO3(aq) + N2O(g) (acidic solution)
b. BrO3-(aq) + N2H4(g) → Br-(aq) + N2(g) (acidic solution)
c. H2O2(aq) + ClO2(aq) → ClO20(aq) _ O2(g) (basic solution)
Complete and balance the following equations, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents. (Recall that the O atoms in hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, have an atypical oxidation state.) H2O21aq2 + ClO21aq2 ¡ ClO2-1aq2 + O21g2 (basic solution)
