Indicate whether the following balanced equations involve oxidation–reduction. If they do, identify the elements that undergo changes in oxidation number. (a) PBr3(l) + 3 H2O(l) → H3PO3(aq) + 3 HBr(aq)

At 900 °C, titanium tetrachloride vapor reacts with molten magnesium metal to form solid titanium metal and molten magnesium chloride. (a) Write a balanced equation for this reaction.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Balancing Chemical Equations

Stoichiometry

Types of Chemical Reactions
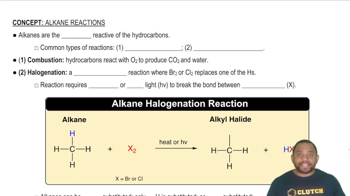
Indicate whether the following balanced equations involve oxidation–reduction. If they do, identify the elements that undergo changes in oxidation number. (b) NaI(aq) + 3 HOCl(aq) → NaIO3(aq) + 3 HCl(aq) (c) 3 SO(1g) + 2 HNO3(aq) + 2 H2O(l) → 3 H2SO4(aq) + 2 NO(g)
Indicate whether the following balanced equations involve oxidation–reduction. If they do, identify the elements that undergo changes in oxidation number. (a) 2 AgNO3(aq) + CoCl2(aq) → 2 AgCl(s) + Co(NO3)2(aq)
Hydrazine (N2H4) and dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4) form a self-igniting mixture that has been used as a rocket propellant. The reaction products are N2 and H2O. (c) Which substance serves as the reducing agent and which as the oxidizing agent?
Complete and balance the following half-reactions. In each case, indicate whether the half-reaction is an oxidation or a reduction. (a) Sn2+(aq) → Sn4+(aq) (acidic solution) (b) TiO2(s) → Ti2+(aq) (acidic solution) (c) ClO3-(aq) → Cl-(aq) (acidic solution) (d) N2(g) → NH4+(aq) (acidic solution)
Complete and balance the following half-reactions in basic solution. In each case, indicate whether the half-reaction is an oxidation or a reduction.
a. OH−(𝑎𝑞)⟶O2(𝑔)
b. SO32−(𝑎𝑞)⟶SO42−(𝑎𝑞)
c. N2(𝑔)⟶NH3(𝑔)
d. HO2−(𝑎𝑞)⟶OH−(𝑎𝑞)
