(b) Can the “fuel” of a fuel cell be a solid?

An iron object is plated with a coating of cobalt to protect against corrosion. Does the cobalt protect the iron by cathodic protection?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
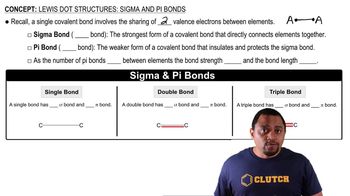
Cathodic Protection
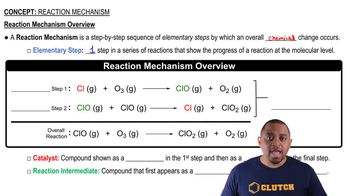
Corrosion Mechanism
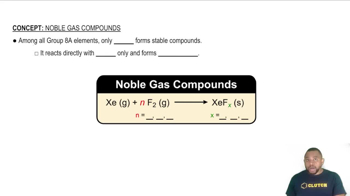
Noble and Reactive Metals
Iron corrodes to produce rust, Fe2O3, but other corrosion products that can form are Fe(O)(OH), iron oxyhydroxide, and magnetite, Fe3O4. (a) What is the oxidation number of Fe in iron oxyhydroxide, assuming oxygen's oxidation number is -2? (b) The oxidation number for Fe in magnetite was controversial for a long time. If we assume that oxygen’s oxidation number is - 2, and Fe has a unique oxidation number, what is the oxidation number for Fe in magnetite? (O)(OH), iron oxyhydroxide, and magnetite, Fe3O4. (c) It turns out that there are two different kinds of Fe in magnetite that have different oxidation numbers. Suggest what these oxidation numbers are and what their relative stoichiometry must be, assuming oxygen’s oxidation number is -2.
Copper corrodes to cuprous oxide, Cu2O, or cupric oxide, CuO, depending on environmental conditions. (a) What is the oxidation state of copper in cuprous oxide?
(c) What process occurs at the anode in the electrolysis of molten NaCl?
