Textbook Question
Give the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following acids: (d) hypochlorous acid (e) iodic acid (f) sulfurous acid.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

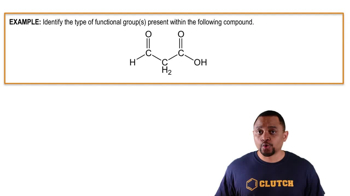
Give the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following acids: (d) hypochlorous acid (e) iodic acid (f) sulfurous acid.
Provide the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following acids: (a) hydroiodic acid (b) chloric acid (c) nitrous acid
Provide the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following acids: (e) HClO4
Give the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following binary molecular substances: (c) XeO3 (d) dinitrogen tetroxide (e) hydrogen cyanide
Give the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following binary molecular substances: (f) tetraphosphorus hexasulfide.