Complete the table by filling in the formula for the ionic compound formed by each pair of cations and anions, as shown for the first pair. Ion Na+ Ca2+ Fe2+ Al3+ O2- Na2O NO3- SO42- AsO43-
Ch.2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 2, Problem 65b
Predict whether each of the following compounds is molecular or ionic: (b) CH3OH
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the types of elements present in the compound CH3OH.
Recognize that CH3OH consists of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms.
Recall that molecular compounds are typically formed between nonmetals.
Note that carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are all nonmetals.
Conclude that CH3OH is a molecular compound because it is composed entirely of nonmetals.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Compounds
Molecular compounds are formed when two or more nonmetals bond together by sharing electrons through covalent bonds. These compounds typically have low melting and boiling points and do not conduct electricity in their solid state. An example is water (H2O), where hydrogen and oxygen share electrons.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Naming Molecular Compounds
Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed when metals and nonmetals react, resulting in the transfer of electrons from the metal to the nonmetal, creating charged ions. These compounds usually have high melting and boiling points and conduct electricity when dissolved in water or molten. Sodium chloride (NaCl) is a classic example of an ionic compound.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ionic Compounds Naming
Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In the case of CH3OH (methanol), the hydroxyl group (-OH) is a functional group that indicates it is an alcohol, a type of molecular compound. Understanding functional groups helps in predicting the properties and reactivity of organic compounds.
Recommended video:
Guided course
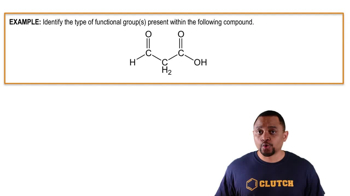
Functional Groups In Chemistry Example
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Complete the table by filling in the formula for the ionic compound formed by each pair of cations and anions, as shown for the first pair. Ion K+ NH4+ Mg2+ Fe3+ Cl- KCl OH- CO32- PO43-
Complete the first row of the table.
Complete the second row of the table.
Complete the third row of the table.
Complete the fourth row of the table.
Textbook Question
Predict whether each of the following compounds is molecular or ionic: (a) B2H6
Textbook Question
Predict whether each of the following compounds is molecular or ionic: (e) CsBr
Textbook Question
Predict whether each of the following compounds is molecular or ionic: (f) NOCl
Textbook Question
Predict whether each of the following compounds is molecular or ionic: (h) Ag2SO4.
