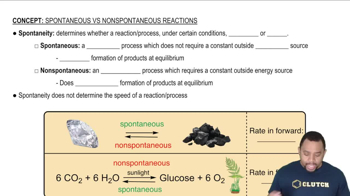
A standard air conditioner involves a refrigerant that is typically now a fluorinated hydrocarbon, such as CH2F2. An air-conditioner refrigerant has the property that it readily vaporizes at atmospheric pressure and is easily compressed to its liquid phase under increased pressure. The operation of an air conditioner can be thought of as a closed system made up of the refrigerant going through the two stages shown here (the air circulation is not shown in this diagram).
During expansion, the liquid refrigerant is released into an expansion chamber at low pressure, where it vaporizes. The vapor then undergoes compression at high pressure back to its liquid phase in a compression chamber. (c) In a central air-conditioning system, one chamber is inside the home and the other is outside. Which chamber is where, and why?