The solubility of CaCO3 is pH dependent. (b) Use the Kb expression for the CO32- ion to determine the equilibrium constant for the reaction CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) ⇌ Ca2+(aq) + HCO3-(aq) + OH-(aq)
Ch.17 - Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 17, Problem 103
The solubility-product constant for barium permanganate, Ba1MnO422, is 2.5 * 10-10. Assume that solid Ba1MnO422 is in equilibrium with a solution of KMnO4. What concentration of KMnO4 is required to establish a concentration of 2.0 * 10-8 M for the Ba2 + ion in solution?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Write the dissolution equation for barium permanganate, BaMnO4, which dissociates into Ba2+ and MnO4- ions in solution: BaMnO4(s) ⇌ Ba2+(aq) + MnO4-(aq).
Express the solubility-product constant (Ksp) for this reaction. Given that Ksp = [Ba2+][MnO4-], substitute the given Ksp value: 2.5 * 10^-10 = [Ba2+][MnO4-].
Substitute the given concentration of Ba2+ ions into the Ksp expression: 2.5 * 10^-10 = (2.0 * 10^-8)[MnO4-].
Solve for the concentration of MnO4- by isolating [MnO4-] on one side of the equation: [MnO4-] = (2.5 * 10^-10) / (2.0 * 10^-8).
Calculate the concentration of MnO4- using the values provided to find the required concentration of KMnO4 in the solution.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)
The solubility product constant (Ksp) is an equilibrium constant that applies to the solubility of sparingly soluble ionic compounds. It is defined as the product of the molar concentrations of the ions, each raised to the power of their coefficients in the balanced equation. For barium permanganate, Ksp helps determine the maximum concentration of Ba2+ ions that can exist in solution at equilibrium.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Solubility Product Constant
Equilibrium in Chemical Reactions
Equilibrium in chemical reactions refers to the state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, resulting in constant concentrations of reactants and products. In the context of solubility, this means that the dissolution of solid barium permanganate and the precipitation of Ba2+ ions occur at the same rate, allowing us to use Ksp to find the concentration of ions in solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chemical Equilibrium Concepts
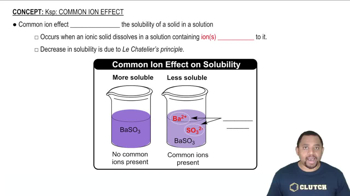
Common Ion Effect
The common ion effect describes the decrease in solubility of a salt when a common ion is added to the solution. In this case, adding KMnO4 introduces MnO4- ions, which affects the solubility of Ba1MnO422 by shifting the equilibrium position. Understanding this effect is crucial for calculating the required concentration of KMnO4 to achieve a specific concentration of Ba2+ ions in solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Common Ion Effect
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Tooth enamel is composed of hydroxyapatite, whose simplest formula is Ca5(PO4)3OH, and whose corresponding 𝐾𝑠𝑝=6.8×10−27. As discussed in the “Chemistry and Life” box on “Tooth Decay and Fluoridation” in Section 17.5, fluoride in fluorinated water or in toothpaste reacts with hydroxyapatite to form fluoroapatite, Ca5(PO4)3F, whose 𝐾𝑠𝑝=1.0×10−60. a. Write the expression for the solubility-constant for hydroxyapatite and for fluoroapatite.
Textbook Question
Calculate the solubility of Mg1OH22 in 0.50 M NH4Cl.
Textbook Question
The solubility product constants of PbSO4 and SrSO4 are 6.3 * 10-7 and 3.2 * 10-7, respectively. What are the values of 3SO4 2 - 4, 3Pb2 + 4, and 3Sr2 + 4 in a solution at equilibrium with both substances?
