Suppose that for the reaction K+L⟶M, you monitor the production of M over time, and then plot the following graph from your data: b. Is the reaction completed at 𝑡=15 min?

Which of the following linear plots do you expect for a reaction A⟶products if the kinetics are a. zero order, [Section 14.3]
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Zero-Order Kinetics
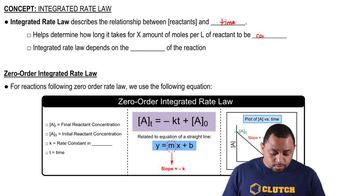
Integrated Rate Law
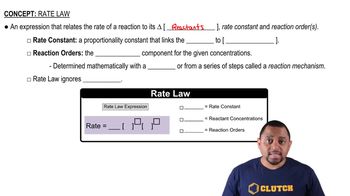
Graphical Representation of Reaction Order

The following diagrams represent mixtures of NO(g) and O2(𝑔). These two substances react as follows:
2 NO(𝑔)+O2(𝑔)⟶2 NO2(𝑔)
It has been determined experimentally that the rate is second order in NO and first order in O2. Based on this fact, which of the following mixtures will have the fastest initial rate? [Section 14.2]
Given the following diagrams at 𝑡=0 min and 𝑡=30 min, b. After four half-life periods for a first-order reaction, what fraction of reactant remains? [Section 14.3]
The accompanying graph shows plots of ln k versus 1>T for two different reactions. The plots have been extrapolated to the y-intercepts. Which reaction (red or blue) has (a) the larger value for Ea,
The accompanying graph shows plots of ln k versus 1/𝑇 for two different reactions. The plots have been extrapolated to the y-intercepts. Which reaction (red or blue) has b. the larger value for the frequency factor, A? [Section 14.4]
