Consider the diagram that follows, which represents two steps in an overall reaction. The red spheres are oxygen, the blue ones are nitrogen, and the green ones are fluorine. d. Write the rate law for the overall reaction if the first step is the slow, rate-determining step. [Section 14.5]
Ch.14 - Chemical Kinetics

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 14, Problem 17b
(b) Name three factors that can affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
1. Concentration of Reactants: The rate of a chemical reaction can be affected by the concentration of the reactants. In general, the higher the concentration of the reactants, the faster the rate of the reaction. This is because a higher concentration means there are more reactant particles per unit volume, which increases the likelihood of collisions between reactant particles, leading to a faster reaction rate.
2. Temperature: The rate of a chemical reaction can also be affected by the temperature. As the temperature increases, the kinetic energy of the particles also increases. This means that the particles move faster and collide more frequently and with greater energy, which can lead to a faster reaction rate.
3. Presence of a Catalyst: A catalyst is a substance that can speed up a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. The catalyst itself is not consumed in the reaction, so it can be used repeatedly. The presence of a catalyst can significantly increase the rate of a chemical reaction.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Concentration of Reactants
The concentration of reactants refers to the amount of a substance in a given volume. Higher concentrations typically lead to an increased rate of reaction because there are more reactant particles available to collide and react with each other, thus increasing the frequency of effective collisions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Calculate Concentration of the Basic Form
Temperature
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance. Increasing the temperature generally increases the rate of a chemical reaction, as higher temperatures provide reactant molecules with more energy, leading to more frequent and energetic collisions that can overcome the activation energy barrier.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Temperature vs Heat
Catalysts
Catalysts are substances that increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. They work by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy, allowing more reactant molecules to participate in the reaction at a given temperature, thus speeding up the overall reaction rate.
Recommended video:
Guided course
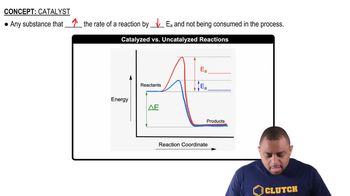
Catalyzed vs. Uncatalyzed Reactions
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Based on the following reaction profile, how many intermediates are formed in the reaction A⟶C? How many transition states are there? Which step, A⟶B or B⟶C, is the faster? For the reaction A⟶C, is Δ𝐸 positive, negative, or zero? [Section 14.5]
Textbook Question
(a) What are the units usually used to express the rates of reactions occurring in solution?
Textbook Question
b. As the temperature increases, does the reaction rate usually increase or decrease?
Textbook Question
(c) As a reaction proceeds, does the instantaneous reaction rate increase or decrease?
