Textbook Question
Which of the following in each pair is likely to be more soluble in water: (a) cyclohexane (C6H12) or glucose (C6H12O6),

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


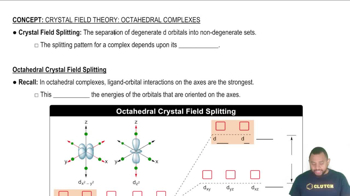
Which of the following in each pair is likely to be more soluble in water: (a) cyclohexane (C6H12) or glucose (C6H12O6),
Which of the following in each pair is likely to be more soluble in water: (b) propionic acid (CH3CH2COOH) or sodium propionate (CH3CH2COONa)
Which of the following in each pair is likely to be more soluble in water: (c) HCl or ethyl chloride (CH3CH2Cl)? Explain in each case.
Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (d) If you take a saturated solution and raise its temperature, you can (usually) add more solute and make the solution even more concentrated.
(a) Calculate the mass percentage of Na2SO4 in a solution containing 10.6 g of Na2SO4 in 483 g of water.