The density of acetonitrile (CH3CN) is 0.786 g/mL and the density of methanol (CH3OH) is 0.791 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 22.5 mL of CH3OH in 98.7 mL of CH3CN. (c) Assuming that the volumes are additive, what is the molarity of CH3OH in the solution?
Ch.13 - Properties of Solutions

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 13, Problem 51b
Calculate the number of moles of solute present in each of the following aqueous solutions: (b) 86.4 g of 0.180 m KCl,
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the given information: mass of solvent (water) is 86.4 g and molality (m) is 0.180 m.
Convert the mass of the solvent from grams to kilograms, since molality is defined as moles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
Use the definition of molality: \( m = \frac{\text{moles of solute}}{\text{kilograms of solvent}} \) to set up the equation for moles of solute.
Rearrange the equation to solve for moles of solute: \( \text{moles of solute} = m \times \text{kilograms of solvent} \).
Substitute the known values into the equation to calculate the moles of solute.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molarity (M)
Molarity is a measure of concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is expressed in units of moles per liter (mol/L). Understanding molarity is essential for calculating the amount of solute in a given volume of solution, which is crucial for solving the problem presented.
Recommended video:
Guided course
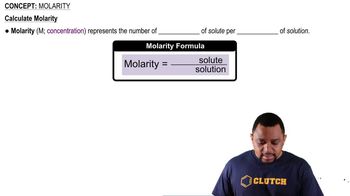
Molarity Concept
Moles of Solute
A mole is a unit in chemistry that represents 6.022 x 10²³ particles (atoms, molecules, etc.). To find the number of moles of solute in a solution, one can use the formula: moles = molarity × volume. This concept is vital for determining how much solute is present in the solution based on its concentration and volume.
Recommended video:
Guided course
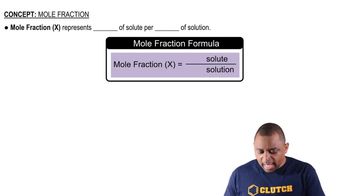
Mole Fraction Formula
Mass and Molar Mass
The mass of a substance is the amount of matter it contains, typically measured in grams. Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). To calculate the number of moles from a given mass, the formula used is: moles = mass (g) / molar mass (g/mol). This relationship is key to solving the problem regarding the amount of KCl in the solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molar Mass Concept
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The density of toluene (C7H8) is 0.867 g/mL, and the density of thiophene (C4H4S) is 1.065 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 8.10 g of thiophene in 250.0 mL of toluene. (a) Calculate the mole fraction of thiophene in the solution.
1
views
Textbook Question
The density of toluene (C7H8) is 0.867 g/mL, and the density of thiophene (C4H4S) is 1.065 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 8.10 g of thiophene in 250.0 mL of toluene. (b) Calculate the molality of thiophene in the solution.
Textbook Question
Calculate the number of moles of solute present in each of the following aqueous solutions: (c) 124.0 g of a solution that is 6.45% glucose (C6H12O6) by mass.
Textbook Question
Calculate the number of moles of solute present in each of the following solutions: (a) 255 mL of 1.50 M HNO3(aq),
