Textbook Question
(a) Calculate the mass percentage of Na2SO4 in a solution containing 10.6 g of Na2SO4 in 483 g of water.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
(a) Calculate the mass percentage of Na2SO4 in a solution containing 10.6 g of Na2SO4 in 483 g of water.
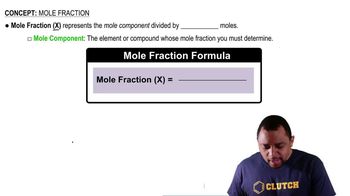
A solution is made containing 20.8 g of phenol (C6H5OH) in 425 g of ethanol (CH3CH2OH). Calculate (a) the mole fraction of phenol,
A solution is made containing 20.8 g of phenol (C6H5OH) in 425 g of ethanol (CH3CH2OH). Calculate (c) the molality of phenol.
Calculate the molarity of the following aqueous solutions: (c) 25.0 mL of 3.50 M HNO3 diluted to 0.250 L.