Which member in each pair has the greater dispersion forces? (b) CO2 or CO, (c) SiH4 or GeH4.

Rationalize the difference in boiling points in each pair: (a) HF (20 °C) and HCl (-85 °C) (b) CHCl3 (61 °C) and CHBr3 (150 °C) (c) Br2 (59 °C) and ICl (97 °C)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Hydrogen Bonding
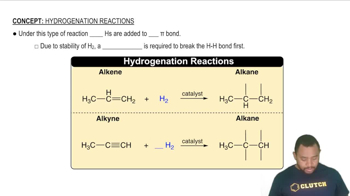
Molecular Weight and Van der Waals Forces

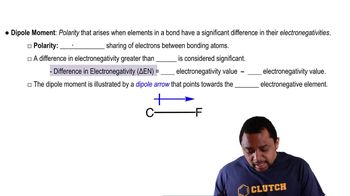
Polarity and Dipole-Dipole Interactions
Which member in each pair has the stronger intermolecular dispersion forces? (a) Br2 or O2 (b) CH3CH2CH2CH2SH or CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2SH (c) CH3CH2CH2Cl or (CH3)2CHCl
(a) What atoms must a molecule contain to participate in hydrogen bonding with other molecules of the same kind? (b) Which of the following molecules can form hydrogen bonds with other molecules of the same kind: CH3F, CH3NH2, CH3OH, CH3Br?
Ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH), the major substance in antifreeze, has a normal boiling point of 198 °C. By comparison, ethyl alcohol (CH3CH2OH) boils at 78 °C at atmospheric pressure. Ethylene glycol dimethyl ether (CH3OCH2CH2OCH3) has a normal boiling point of 83 °C, and ethyl methyl ether (CH3CH2OCH3) has a nomral boiling point of 11 °C. (a) Explain why replacement of a hydrogen on the oxygen by a CH3 group generally results in a lower boiling point.
Ethylene glycol (HOCH2CH2OH), the major substance in antifreeze, has a normal boiling point of 198 °C. By comparison, ethyl alcohol (CH3CH2OH) boils at 78 °C at atmospheric pressure. Ethylene glycol dimethyl ether (CH3OCH2CH2OCH3) has a normal boiling point of 83 °C, and ethyl methyl ether (CH3CH2OCH3) has a nomral boiling point of 11 °C. (b) What are the major factors responsible for the difference in boiling points of the two ethers?
Based on the type or types of intermolecular forces, predict the substance in each pair that has the higher boiling point: (a) propane (C3H8) or n-butane (C4H10) (b) diethyl ether (CH3CH2OCH2CH3) or 1-butanol (CH3CH2CH2CH2OH) (c) sulfur dioxide (SO2) or sulfur trioxide (SO3) (d) phosgene (Cl2CO) or formaldehyde (H2CO)
