Hurricane Wilma of 2005 is the most intense hurricane on record in the Atlantic basin, with a low-pressure reading of 882 mbar (millibars). Convert this reading into (a) atmospheres.

If the atmospheric pressure is 0.995 atm, what is the pressure of the enclosed gas in each of the three cases depicted in the drawing? Assume that the gray liquid is mercury. (i)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Atmospheric Pressure

Hydrostatic Pressure
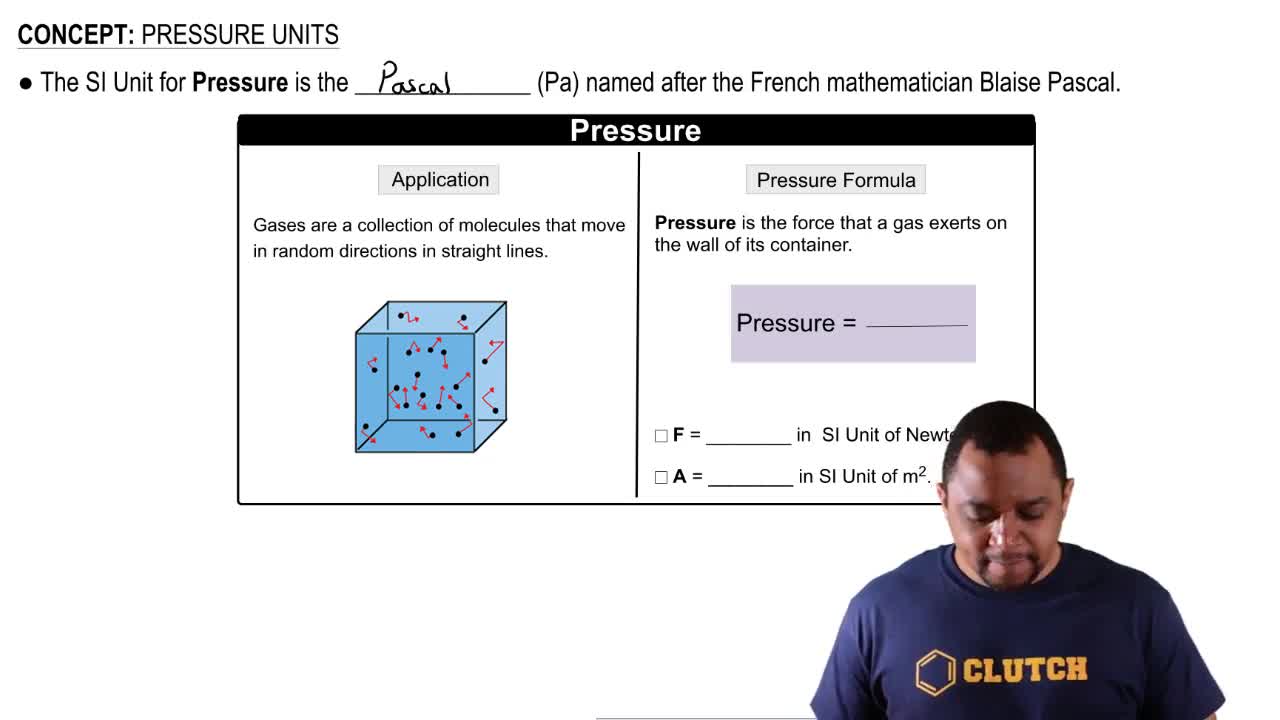
Manometer
Hurricane Wilma of 2005 is the most intense hurricane on record in the Atlantic basin, with a low-pressure reading of 882 mbar (millibars). Convert this reading into (b) torr.
Hurricane Wilma of 2005 is the most intense hurricane on record in the Atlantic basin, with a low-pressure reading of 882 mbar (millibars). Convert this reading into (c) inches of Hg.
If the atmospheric pressure is 0.995 atm, what is the pressure of the enclosed gas in each of the three cases depicted in the drawing? Assume that the gray liquid is mercury. (ii)
An open-end manometer containing mercury is connected to a container of gas, as depicted in Sample Exercise 10.2. What is the pressure of the enclosed gas in torr in each of the following situations? (a) The mercury in the arm attached to the gas is 15.4 mm higher than in the one open to the atmosphere; atmospheric pressure is 0.985 atm.
If a car tire is filled to a pressure of 32.0 lb/in.2 (psi) measured at 75°F, what will be the tire pressure if the tires heat up to 120°F during driving?
