A sample of 5.00 mL of diethyl ether (C2H5OC2H5,density=0.7134 g/mL) is introduced into a 6.00-L vessel that already contains a mixture of N2 and O2, whose partial pressures are 𝑃N2=0.751atm and 𝑃O2=0.208atm. The temperature is held at 35.0°C, and the diethyl ether totally evaporates. b. Calculate the total pressure in the container.

At an underwater depth of 250 ft, the pressure is 8.38 atm. What should the mole percent of oxygen be in the diving gas for the partial pressure of oxygen in the mixture to be 0.21 atm, the same as in air at 1 atm?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Partial Pressure

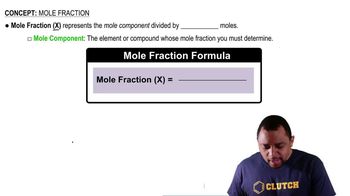
Mole Fraction
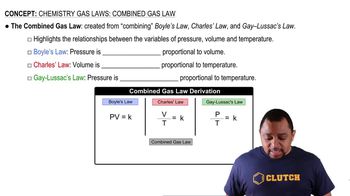
Gas Laws
A rigid vessel containing a 3:1 mol ratio of carbon dioxide and water vapor is held at 200°C where it has a total pressure of 2.00 atm. If the vessel is cooled to 10°C so that all of the water vapor condenses, what is the pressure of carbon dioxide? Neglect the volume of the liquid water that forms on cooling.
At an underwater depth of 250 ft, the pressure is 8.38 atm. What should the mole percent of oxygen be in the diving gas for the partial pressure of oxygen in the mixture to be 0.21 atm, the same as in air at 1 atm?
(a) What are the mole fractions of N2 in a mixture of 15.08 g of O2, 8.17 g of N2, and 2.64 g of H2?
(a) What are the mole fractions of O2 in a mixture of 15.08 g of O2, 8.17 g of N2, and 2.64 g of H2?
(a) What are the mole fractions of H2 in a mixture of 15.08 g of O2, 8.17 g of N2, and 2.64 g of H2?
