The distance from Earth to the Moon is approximately 240,000 mi. (a) What is this distance in meters?

The distance from Earth to the Moon is approximately 240,000 mi. (d) Earth travels around the Sun at an average speed of 29.783 km/s. Convert this speed to miles per hour.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
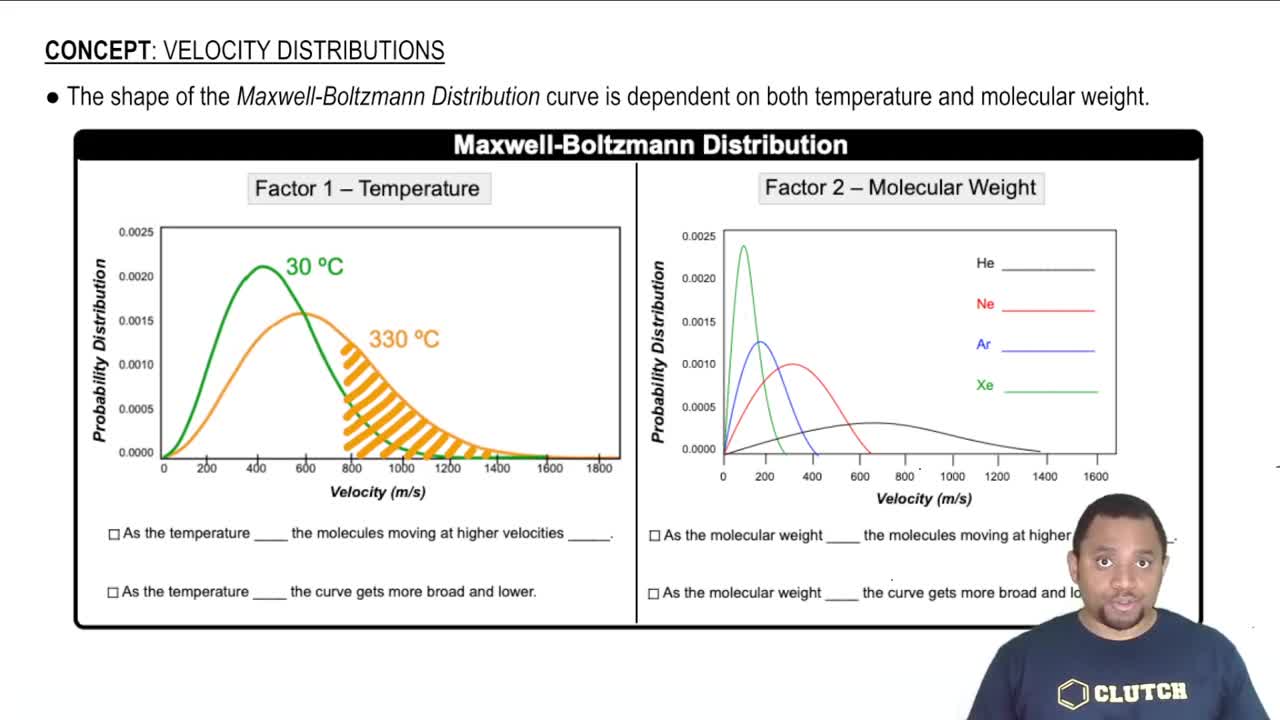
Key Concepts
Unit Conversion

Speed and Velocity
Dimensional Analysis

The distance from Earth to the Moon is approximately 240,000 mi. (b) The peregrine falcon has been measured as traveling up to 350 km/ hr in a dive. If this falcon could fly to the Moon at this speed, how many seconds would it take?
The distance from Earth to the Moon is approximately 240,000 mi. (c) The speed of light is 3.00 ⨉ 108 m/s. How long does it take for light to travel from Earth to the Moon and back again?
Which of the following would you characterize as a pure or nearly pure substance?
a. baking powder
b. lemon juice
c. propane gas, used in outdoor gas grills
d. aluminum foil
e. ibuprofen
f. bourbon whiskey
g. helium gas
h. clear water pumped from a deep aquifer
The U.S. quarter has a mass of 5.67 g and is approximately 1.55 mm thick. (a) How many quarters would have to be stacked to reach 575 ft, the height of the Washington Monument?
