In the lime soda process once used in large scale munici-pal water softening, calcium hydroxide prepared from lime and sodium carbonate are added to precipitate Ca2+ as CaCO3(s) and Mg2+ as Mg(OH)2(s): Ca2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → CaCO3(s) Mg2+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) → MgOH2(aq) How many moles of Ca(OH)2 and Na2CO3 should be added to soften (remove the Ca2+ and Mg2+) 1200 L of water in which [Ca2+] = 5.0x10-4 M and [Mg2+] = 7.0x10-4 M?
Ch.18 - Chemistry of the Environment

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 18, Problem 55
One of the principles of green chemistry is that it is better to use as few steps as possible in making new chemicals. In what ways does following this rule advance the goals of green chemistry? How does this principle relate to energy efficiency?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the principles of green chemistry, which aim to reduce the environmental impact of chemical processes and products by minimizing waste, energy usage, and hazardous substances.
Step 2: Recognize that reducing the number of steps in a chemical synthesis can lead to fewer opportunities for waste generation and the use of hazardous reagents, aligning with the goals of green chemistry.
Step 3: Consider how each step in a chemical process typically requires energy input, such as heating, cooling, or mixing, and how reducing the number of steps can decrease the overall energy consumption of the process.
Step 4: Explore the concept of atom economy, which is related to the efficiency of a chemical reaction in terms of how well the atoms of the starting materials are utilized in the final product, and how fewer steps can improve atom economy.
Step 5: Reflect on how minimizing steps can lead to more streamlined processes, reducing the need for purification and separation, which often require additional energy and resources, thus enhancing energy efficiency.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Green Chemistry Principles
Green chemistry focuses on designing chemical processes and products that minimize the use and generation of hazardous substances. One of its key principles is to reduce the number of steps in chemical synthesis, which can lead to less waste, lower energy consumption, and a reduced environmental impact. By adhering to this principle, chemists can create more sustainable and efficient chemical processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
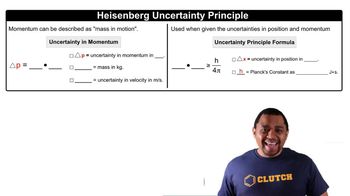
Uncertainty Principle Formula
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency in chemical processes refers to the amount of energy required to produce a given amount of product. Fewer steps in a synthesis typically mean less energy is consumed overall, as each reaction step often requires energy input for heating, cooling, or other processes. By minimizing the number of steps, green chemistry not only conserves energy but also reduces the carbon footprint associated with chemical manufacturing.
Recommended video:
Guided course
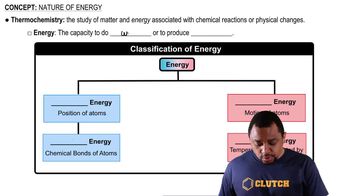
Nature of Energy
Waste Reduction
Reducing waste is a fundamental goal of green chemistry, as waste can be harmful to the environment and costly to manage. By using fewer steps in chemical synthesis, the amount of by-products and unreacted materials is minimized, leading to less waste generation. This principle aligns with the broader objectives of sustainability and environmental protection, making chemical processes cleaner and more responsible.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Standard Reduction Potentials
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
(a) What are trihalomethanes (THMs)? (b) Draw the Lewis structures of two example THMs.
Textbook Question
A reaction for converting ketones to lactones, called the Baeyer–Villiger reaction,
is used in the manufacture of plastics and pharmaceu- ticals. 3-Chloroperbenzoic acid is shock-sensitive, how- ever, and prone to explode. Also, 3-chlorobenzoic acid is a waste product. An alternative process being developed uses hydrogen peroxide and a catalyst consisting of tin deposited within a solid support. The catalyst is readily recovered from the reaction mixture. (a) What would you expect to be the other product of oxidation of the ketone to lactone by hydrogen peroxide?
