Textbook Question
(a) What is the difference between chlorofluorocarbons and hydrofluorocarbons?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance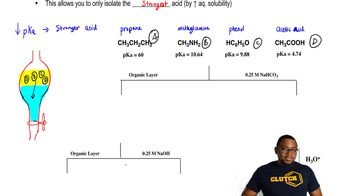
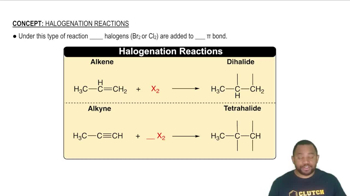

(a) What is the difference between chlorofluorocarbons and hydrofluorocarbons?
(a) When chlorine atoms react with atmospheric ozone, what are the products of the reaction?
(b) Based on average bond enthalpies, would you expect a photon capable of dissociating a C-Cl bond to have sufficient energy to dissociate a C-Br bond?