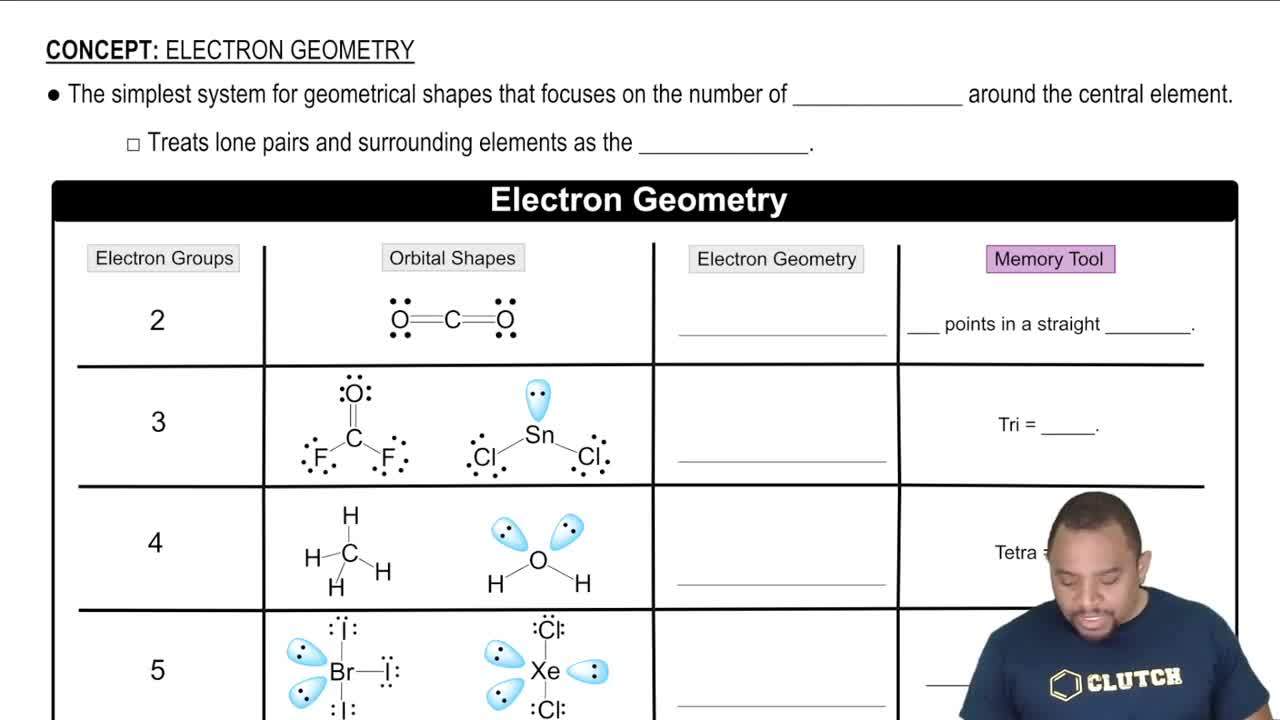
The structure of borazine, B3N3H6, is a six-membered ring of alternating B and N atoms. There is one H atom bonded to each B and to each N atom. The molecule is planar. (a) Write a Lewis structure for borazine in which the formal charge on every atom is zero.

The highest occupied molecular orbital of a molecule is abbreviated as the HOMO. The lowest unoccupied molecular orbital in a molecule is called the LUMO. Experimentally, one can measure the difference in energy between the HOMO and LUMO by taking the electronic absorption (UV-visible) spectrum of the molecule. Peaks in the electronic absorption spectrum can be labeled as π→π*, σ→σ*, and so on, corresponding to electrons being promoted from one orbital to another. The HOMO-LUMO transition corresponds to molecules going from their ground state to their first excited state. (a) Write out the molecular orbital valence electron configurations for the ground state and first excited state for N₂. (b) Is N₂ paramagnetic or diamagnetic in its first excited state? (d) Calculate the energy of the HOMO-LUMO transition in part (a) in terms of kJ/mol. (e) Is the N≡N bond in the first excited state stronger or weaker compared to that in the ground state?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
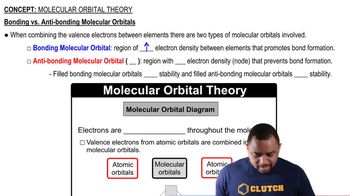
Molecular Orbital Theory
Electronic Absorption Spectroscopy
Paramagnetism and Diamagnetism

The structure of borazine, B3N3H6, is a six-membered ring of alternating B and N atoms. There is one H atom bonded to each B and to each N atom. The molecule is planar. (c) What are the formal charges on the atoms in the Lewis structure from part (b)? Given the electronegativities of B and N, do the formal charges seem favorable or unfavorable? What are the formal charges on the atoms in the Lewis structure from part (b)?
The structure of borazine, B3N3H6, is a six-membered ring of alternating B and N atoms. There is one H atom bonded to each B and to each N atom. The molecule is planar. (e) What are the hybridizations at the B and N atoms in the Lewis structures from parts (a) and (b)? Would you expect the molecule to be planar for both Lewis structures? Would you expect the molecule to be planar for both Lewis structures?
The highest occupied molecular orbital of a molecule is abbreviated as the HOMO. The lowest unoccupied molecular orbital in a molecule is called the LUMO. Experimentally, one can measure the difference in energy between the HOMO and LUMO by taking the electronic absorption (UV-visible) spectrum of the molecule. Peaks in the electronic absorption spectrum can be labeled as π2p-π2p*, σs-σ2s*, and so on, corresponding to electrons being promoted from one orbital to another. The HOMO-LUMO transition corresponds to molecules going from their ground state to their first excited state. (c) The electronic absorption spectrum of the N2 molecule has the lowest energy peak at 170 nm. To what orbital transition does this correspond?
One of the molecular orbitals of the H2- ion is sketched below:
(a) Is the molecular orbital a s or p MO? Is it bonding or antibonding?
One of the molecular orbitals of the H2- ion is sketched below: (d) Compared to the H¬H bond in H2, the H¬H bond in H2- is expected to be which of the following: (i) Shorter and stronger, (ii) longer and stronger, (iii) shorter and weaker, (iv) longer and weaker, or (v) the same length and strength?
