a) Predict the electron-domain geometry around the central S atom in SF2, SF4, and SF6.

Sodium azide is a shock-sensitive compound that releases N2 upon physical impact. The compound is used in automobile airbags. The azide ion is N3-. (a) Draw the Lewis structure of the azide ion that minimizes formal charge (it does not form a triangle). Is it linear or bent?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Lewis Structures

Formal Charge

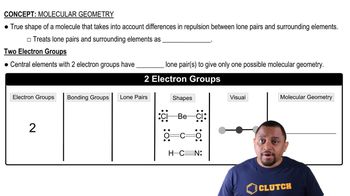
Molecular Geometry
(b) The anion IO4- has a tetrahedral structure: three oxygen atoms form double bonds with the central iodine atom and one oxygen atom which carries a negative charge forms a single bond. Predict the molecular geometry of IO65-.
Which of the following statements about hybrid orbitals is or are true? (i) After an atom undergoes sp hybridization, there is one unhybridized p orbital on the atom, (ii) Under sp2 hybridization, the large lobes point to the vertices of an equilateral triangle, and (iii) The angle between the large lobes of sp3 hybrids is 109.5°.
Sodium azide is a shock-sensitive compound that releases N2 upon physical impact. The compound is used in automobile airbags. The azide ion is N3-. (b) State the hybridization of the central N atom in the azide ion.
In ozone, O3, the two oxygen atoms on the ends of the molecule are equivalent to one another. (d) How many electrons are delocalized in the p system of ozone?
