The iodine bromide molecule, IBr, is an interhalogen compound. Assume that the molecular orbitals of IBr are analogous to the homonuclear diatomic molecule F2. (a) Which valence atomic orbitals of I and of Br are used to construct the MOs of IBr?

An AB2 molecule is described as having a tetrahedral geometry. (a) How many nonbonding domains are on atom A?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
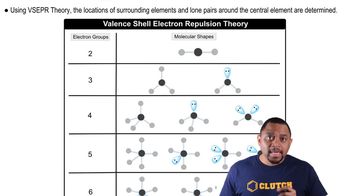
Molecular Geometry
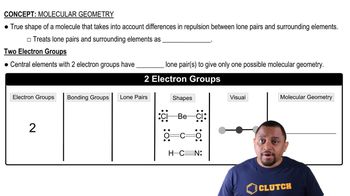
VSEPR Theory
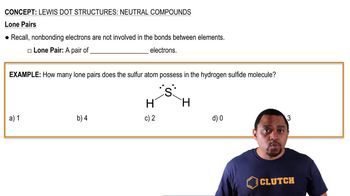
Nonbonding Domains
The iodine bromide molecule, IBr, is an interhalogen compound. Assume that the molecular orbitals of IBr are analogous to the homonuclear diatomic molecule F2. (c) One of the valence MOs of IBr is sketched here. Why are the atomic orbital contributions to this MO different in size?
An AB2 molecule is described as having a tetrahedral geometry. (b) Based on the information given, which of the following is the molecular geometry of the molecule: (i) linear, (ii) bent, (iii) trigonal planar, or (iv) tetrahedral?
Consider the following XF4 ions: PF4-, BrF4-, ClF4+, and AlF4-. (a) Which of the ions have more than an octet of electrons around the central atom?
Consider the following XF4 ions: PF4-, BrF4-, ClF4+, and AlF4-. (b) For which of the ions will the electron-domain and molecular geometries be the same?
