Textbook Question
State whether each of these statements is true or false. (e) The longer the bond, the more energy is stored chemical bonds.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance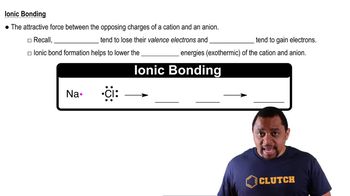


State whether each of these statements is true or false. (e) The longer the bond, the more energy is stored chemical bonds.