Consider the formate ion, HCO2-, which is the anion formed when formic acid loses an H+ ion. The H and the two O atoms are bonded to the central C atom. (c) Would you predict that the C—O bond lengths in the formate ion would be longer or shorter relative to those in CO2?

True or false: (a) The C¬C bonds in benzene are all the same length and correspond to typical single C¬C bond lengths. (b) The C¬C bond in acetylene, HC≡CH, is longer than the average C¬C bond length in benzene.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Resonance in Benzene

Bond Lengths and Types
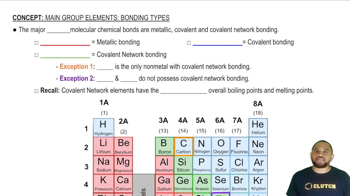
Comparative Bond Lengths

Predict the ordering, from shortest to longest, of the bond lengths in CO, CO2, and CO32- .
Based on Lewis structures, predict the ordering, from shortest to longest, of N¬O bond lengths in NO+, NO2-, and NO3-.
Mothballs are composed of naphthalene, C10H8, a molecule that consists of two six-membered rings of carbon fused along an edge, as shown in this incomplete Lewis structure:(a) Draw all of the resonance structures of naphthalene. How many are there?
Mothballs are composed of naphthalene, C10H8, a molecule that consists of two six-membered rings of carbon fused along an edge, as shown in this incomplete Lewis structure:
(b) Do you expect the C—C bond lengths in the molecule to be similar to those of C—C single bonds, C ═C double bonds, or intermediate between C—C single and C ═C double bonds?
Mothballs are composed of naphthalene, C10H8, a molecule that consists of two six-membered rings of carbon fused along an edge, as shown in this incomplete Lewis structure:
(c) Not all of the C—C bond lengths in naphthalene are equivalent. Based on your resonance structures, how many C—C bonds in the molecule do you expect to be shorter than the others?
