Textbook Question
For each of these Lewis symbols, indicate the group in the periodic table in which the element X belongs: (a)
3
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
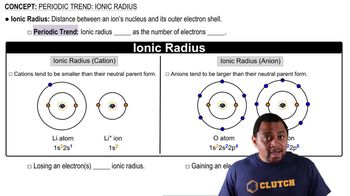

For each of these Lewis symbols, indicate the group in the periodic table in which the element X belongs: (a)
A portion of a two-dimensional 'slab' of NaCl(s) is shown here (see Figure 8.2) in which the ions are numbered. (a) Which colored balls must represent sodium ions?
A portion of a two-dimensional 'slab' of NaCl(s) is shown here (see Figure 8.2) in which the ions are numbered. (d) Consider ion 5. How many repulsive interactions are shown for it?
The orbital diagram that follows shows the valence electrons for a 2+ ion of an element. (a) What is the element?